A phenotypic screen of the Global Health Priority Box identifies an insecticide with anthelmintic activity
- PMID: 38486232
- PMCID: PMC10938758
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-024-06183-y
A phenotypic screen of the Global Health Priority Box identifies an insecticide with anthelmintic activity
Abstract
Background: Infection with parasitic nematodes (helminths), particularly those of the order Strongylida (such as Haemonchus contortus), can cause significant and burdensome diseases in humans and animals. Widespread drug (anthelmintic) resistance in livestock parasites, the absence of vaccines against most of these nematodes, and a lack of new and effective chemical entities on the commercial market demands the discovery of new anthelmintics. In the present study, we searched the Global Health Priority Box (Medicines for Malaria Venture) for new candidates for anthelmintic development.
Methods: We employed a whole-organism, motility-based phenotypic screening assay to identify compounds from the Global Health Priority Box with activity against larvae of the model parasite H. contortus, and the free-living comparator nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Hit compounds were further validated via dose-response assays, with lead candidates then assessed for nematocidal activity against H. contortus adult worms, and additionally, for cytotoxic and mitotoxic effects on human hepatoma (HepG2) cells.
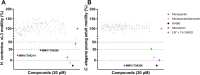
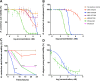
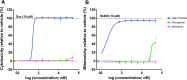
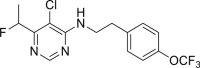
Results: The primary screen against H. contortus and C. elegans revealed or reidentified 16 hit compounds; further validation established MMV1794206, otherwise known as 'flufenerim', as a significant inhibitor of H. contortus larval motility (half-maximal inhibitory concentration [IC50] = 18 μM) and development (IC50 = 1.2 μM), H. contortus adult female motility (100% after 12 h of incubation) and C. elegans larval motility (IC50 = 0.22 μM). Further testing on a mammalian cell line (human hepatoma HepG2 cells), however, identified flufenerim to be both cytotoxic (half-maximal cytotoxic concentration [CC50] < 0.7 μM) and mitotoxic (half-maximal mitotoxic concentration [MC50] < 0.7 μM).
Conclusions: The in vitro efficacy of MMV1794206 against the most pathogenic stages of H. contortus, as well as the free-living C. elegans, suggests the potential for development as a broad-spectrum anthelmintic compound; however, the high toxicity towards mammalian cells presents a significant hindrance. Further work should seek to establish the protein-drug interactions of MMV1794206 in a nematode model, to unravel the mechanism of action, in addition to an advanced structure-activity relationship investigation to optimise anthelmintic activity and eliminate mammalian cell toxicity.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; Haemonchus contortus; Anthelmintics; Antiparasitics; Drug discovery; Flufenerim; Global Health Priority Box; Nematodes; Phenotypic screening.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Institutes for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Intestinal nematode infections – level 3 cause. 2020. https://www.healthdata.org/results/gbd_summaries/2019/intestinal-nematod.... Accessed 12 Sep 2023.
-
- World Health Organization . Ending the neglect to attain the sustainable development goals: a road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
-
- Shephard R, Ware JW, Blomfield B, Neithe G. Priority list of endemic diseases for the red meat industry—2022 update. North Sydney: Meat & Livestock Australia Limited; 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

