Opportunities, challenges, and future directions of large language models, including ChatGPT in medical education: a systematic scoping review
- PMID: 38486402
- PMCID: PMC11035906
- DOI: 10.3352/jeehp.2024.21.6
Opportunities, challenges, and future directions of large language models, including ChatGPT in medical education: a systematic scoping review
Abstract
Background: ChatGPT is a large language model (LLM) based on artificial intelligence (AI) capable of responding in multiple languages and generating nuanced and highly complex responses. While ChatGPT holds promising applications in medical education, its limitations and potential risks cannot be ignored.
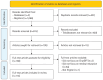
Methods: A scoping review was conducted for English articles discussing ChatGPT in the context of medical education published after 2022. A literature search was performed using PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, and Web of Science databases, and information was extracted from the relevant studies that were ultimately included.
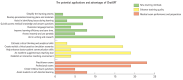
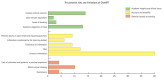
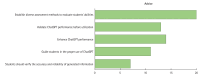
Results: ChatGPT exhibits various potential applications in medical education, such as providing personalized learning plans and materials, creating clinical practice simulation scenarios, and assisting in writing articles. However, challenges associated with academic integrity, data accuracy, and potential harm to learning were also highlighted in the literature. The paper emphasizes certain recommendations for using ChatGPT, including the establishment of guidelines. Based on the review, 3 key research areas were proposed: cultivating the ability of medical students to use ChatGPT correctly, integrating ChatGPT into teaching activities and processes, and proposing standards for the use of AI by medical students.
Conclusion: ChatGPT has the potential to transform medical education, but careful consideration is required for its full integration. To harness the full potential of ChatGPT in medical education, attention should not only be given to the capabilities of AI but also to its impact on students and teachers.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Attention; Data accuracy; Medical education; Medical students.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Deng J, Lin Y. The benefits and challenges of ChatGPT: an overview. Front Comput Intell Syst. 2022;2:81–83. doi: 10.54097/fcis.v2i2.4465. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

