DL-3- n-butylphthalide attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 38486757
- PMCID: PMC10938138
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27644
DL-3- n-butylphthalide attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
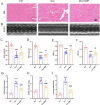
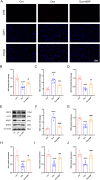
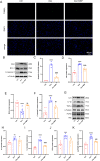
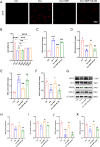
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a widely used chemotherapeutic drug known to cause dose-dependent myocardial toxicity, which limits its clinical potential. DL-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP), a substance extracted from celery seed species, has a number of pharmacological properties, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic actions. However, whether NBP can protect against DOX-induced acute myocardial toxicity is still unclear. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate the potential protective effects of NBP against DOX-induced acute myocardial injury and its underlying mechanism. By injecting 15 mg/kg of DOX intraperitoneally, eight-week-old male C57BL6 mice suffered an acute myocardial injury. The treatment group of mice received 80 mg/kg NBP by gavage once daily for 14 days. To mimic the cardiotoxicity of DOX, 1uM DOX was administered to H9C2 cells in vitro. In comparison to the DOX group, the results showed that NBP improved cardiac function and decreased serum levels of cTnI, LDH, and CK-MB. Additionally, HE staining demonstrated that NBP attenuated cardiac fibrillar lysis and breakage in DOX-treated mouse hearts. Western blotting assay and immunofluorescence staining suggested that NBP attenuated DOX-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation both in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, NBP significantly upregulated the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, while the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 prevented NBP from protecting the myocardium from DOX-induced myocardial toxicity in vitro. In conclusion, Our results indicate that NBP alleviates DOX-induced myocardial toxicity by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: DL-3-n-Butylphthalide; Doxorubicin; Myocardial toxicity; Nrf2; Oxidative stress.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by inhibiting Nrf2/Keap1 complex formation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 29;16:1542296. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542296. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40365306 Free PMC article.
-
Natural compound glycyrrhetinic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 Nov;106:154407. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154407. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36070662
-
Galangin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase 1 signaling pathway to suppress oxidative stress and inflammation.Phytother Res. 2023 Dec;37(12):5854-5870. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7991. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 37655750
-
Tanshinone I inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating Nrf2 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 Nov;106:154439. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154439. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36108374
-
Neuroprotective Effects of dl-3-n-Butylphthalide against Doxorubicin-Induced Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Behavioral Changes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Aug 16;2018:9125601. doi: 10.1155/2018/9125601. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30186550 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Protective effect of Lonicerae japonicae flos extract against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Aug 20;44(8):1571-1581. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.16. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39276053 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Alginate Oligosaccharides Protect Gastric Epithelial Cells against Oxidative Stress Damage through Induction of the Nrf2 Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 20;13(5):618. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050618. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790723 Free PMC article.
-
Trillin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 8;20(4):e0321546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321546. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40198734 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of NRF2 Inhibitors-Retinoic Acid, K67, and ML-385-In Overcoming Doxorubicin Resistance in Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10257. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910257. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408587 Free PMC article.
-
[Experimental study on promotion of peripheral nerve regeneration by selenium-methylselenocysteine].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 15;38(5):598-607. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202402031. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38752248 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Benjanuwattra J., Siri-Angkul N., Chattipakorn S.C., Chattipakorn N. Doxorubicin and its proarrhythmic effects: a comprehensive review of the evidence from experimental and clinical studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2020;151 - PubMed
-
- Narayan H.K., Finkelman B., French B., Plappert T., Hyman D., Smith A.M., et al. Detailed echocardiographic Phenotyping in breast cancer patients: associations with ejection fraction decline, recovery, and heart failure symptoms over 3 Years of follow-up. Circulation. 2017;135(15):1397–1412. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Henriksen P.A. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: an update on mechanisms, monitoring and prevention. Heart. 2018;104(12):971–977. - PubMed
-
- Cvetkovic R.S., Scott L.J. Dexrazoxane : a review of its use for cardioprotection during anthracycline chemotherapy. Drugs. 2005;65(7):1005–1024. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

