The role of N-glycosylation in cancer
- PMID: 38486989
- PMCID: PMC10935144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.10.014
The role of N-glycosylation in cancer
Abstract
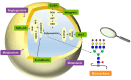
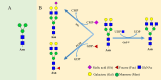
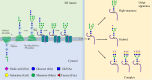
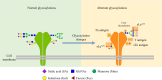
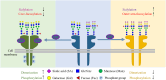
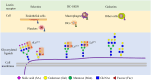
Despite advances in understanding the development and progression of cancer in recent years, there remains a lack of comprehensive characterization of the cancer glycoproteome. Glycoproteins play an important role in medicine and are involved in various human disease conditions including cancer. Glycan-moieties participate in fundamental cancer processes like cell signaling, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Aberrant N-glycosylation significantly impacts cancer processes and targeted therapies in clinic. Therefore, understanding N-glycosylation in a tumor is essential for comprehending disease progression and discovering anti-cancer targets and biomarkers for therapy monitoring and diagnosis. This review presents the fundamental process of protein N-glycosylation and summarizes glycosylation changes in tumor cells, including increased terminal sialylation, N-glycan branching, and core-fucosylation. Also, the role of N-glycosylation in tumor signaling pathways, migration, and metabolism are discussed. Glycoproteins and glycopeptides as potential biomarkers for early detection of cancer based on site specificity have been introduced. Collectively, understanding and exploring the cancer glycoproteome, along with its role in medicine, implication in cancer and other human diseases, highlights the significance of N-glycosylation in tumor processes, necessitating further research for potential anti-cancer targets and biomarkers.
Keywords: Cancer angiogenesis; Cancer biomarkers; Cancer metabolism; Cancer signaling; N-Glycosylated proteins.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cancer . Feb 3, 2022. World health organization.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer Available from:
-
- Adamczyk B., Tharmalingam T., Rudd P.M. Glycans as cancer biomarkers. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2012;1820:1347–1353. - PubMed
-
- Büll C., den Brok M.H., Adema G.J. Sweet escape: sialic acids in tumor immune evasion. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2014;1846:238–246. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

