Biomimetic "Gemini nanoimmunoregulators" orchestrated for boosted photoimmunotherapy by spatiotemporally modulating PD-L1 and tumor-associated macrophages
- PMID: 38486995
- PMCID: PMC10935025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.11.005
Biomimetic "Gemini nanoimmunoregulators" orchestrated for boosted photoimmunotherapy by spatiotemporally modulating PD-L1 and tumor-associated macrophages
Abstract
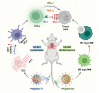
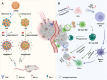
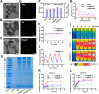
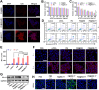
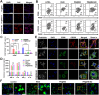
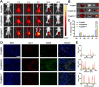
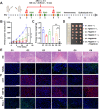
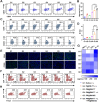
A novel strategy of not only stimulating the immune cycle but also modulating the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment is of vital importance to efficient cancer immunotherapy. Here, a new type of spatiotemporal biomimetic "Gemini nanoimmunoregulators" was engineered to activate robust systemic photoimmunotherapy by integrating the triple-punch of amplified immunogenic cell death (ICD), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) phenotype reprogramming and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) degradation. The "Gemini nanoimmunoregulators" PM@RM-T7 and PR@RM-M2 were constructed by taking the biocompatible mesoporous polydopamine (mPDA) as nanovectors to deliver metformin (Met) and toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist resiquimod (R848) to cancer cells and TAMs by specific biorecognition via wrapping of red blood cell membrane (RM) inlaid with T7 or M2 peptides. mPDA/Met@RM-T7 (abbreviated as PM@RM-T7) was constructed to elicit an amplified in situ ICD effect through the targeted PTT and effectively stimulated the anticancer immunity. Meanwhile, PD-L1 on the remaining cancer cells was degraded by the burst metformin to prevent immune evasion. Subsequently, mPDA/R848@RM-M2 (abbreviated as PR@RM-M2) specifically recognized TAMs and reset the phenotype from M2 to M1 state, thus disrupting the immunosuppressive microenvironment and further boosting the function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. This pair of sister nanoimmunoregulators cooperatively orchestrated the comprehensive anticancer activity, which remarkably inhibited the growth of primary and distant 4T1 tumors and prevented malignant metastasis. This study highlights the spatiotemporal cooperative modalities using multiple nanomedicines and provides a new paradigm for efficient cancer immunotherapy against metastatic-prone tumors.
Keywords: Amplified immunogenic cell death; Biomimetic immunoregulator; Immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment; Metastasis inhibition; PD-L1 degradation; Spatiotemporal delivery; TAMs phenotype reversion; Targeted photothermal therapy.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functionalized biomimetic nanoparticles combining programmed death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 blockade with photothermal ablation for enhanced colorectal cancer immunotherapy.Acta Biomater. 2023 Feb;157:451-466. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.11.043. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36442821
-
A biomimetic nanoplatform for precise reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages and NIR-II mediated antitumor immune activation.Acta Biomater. 2023 May;162:85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.03.021. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36948328
-
Peptide-guided resiquimod-loaded lignin nanoparticles convert tumor-associated macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype for enhanced chemotherapy.Acta Biomater. 2021 Oct 1;133:231-243. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.09.038. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33011297
-
Tumor-associated macrophages in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: recent research progress.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 18;15:1382256. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1382256. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38957393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triple negative breast cancer: Key role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in regulating the activity of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018 Jan;1869(1):78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29126881 Review.
Cited by
-
A phosphoglycerate mutase 1 allosteric inhibitor restrains TAM-mediated colon cancer progression.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Nov;14(11):4819-4831. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.09.007. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39664444 Free PMC article.
-
Smart biomimetic "nano-med-fireman" blocking inflammation and lactate metabolism crosstalk for normalized spatiotemporal photo-immunotherapy.Bioact Mater. 2025 May 21;51:431-449. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.012. eCollection 2025 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40496624 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging advances in drug delivery systems (DDSs) for optimizing cancer complications.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Dec 5;30:101375. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101375. eCollection 2025 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39759851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotherapeutics for Macrophage Network Modulation in Tumor Microenvironments: Targets and Tools.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 19;19:13615-13651. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S491573. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39717515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoresponsive Multirole Nanoweapon Camouflaged by Hybrid Cell Membrane Vesicles for Efficient Antibacterial Therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Pneumonia and Wound.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(35):e2403101. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403101. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39007186 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

