B-cell-depleted patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection: combination therapy or monotherapy? A real-world experience
- PMID: 38487021
- PMCID: PMC10937561
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1344267
B-cell-depleted patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection: combination therapy or monotherapy? A real-world experience
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of the study was to describe a cohort of B-cell-depleted immunocompromised (IC) patients with prolonged or relapsing COVID-19 treated with monotherapy or combination therapy.
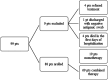
Methods: This is a multicenter observational retrospective study conducted on IC patients consecutively hospitalized with a prolonged or relapsing SARS-CoV-2 infection from November 2020 to January 2023. IC COVID-19 subjects were stratified according to the monotherapy or combination anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapy received.
Results: Eighty-eight patients were enrolled, 19 under monotherapy and 69 under combination therapy. The study population had a history of immunosuppression (median of 2 B-cells/mm3, IQR 1-24 cells), and residual hypogammaglobulinemia was observed in 55 patients. A reduced length of hospitalization and time to negative SARS-CoV-2 molecular nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) in the combination versus monotherapy group was observed. In the univariable and multivariable analyses, the percentage change in the rate of days to NPS negativity showed a significant reduction in patients receiving combination therapy compared to those receiving monotherapy.
Conclusion: In IC persistent COVID-19 patients, it is essential to explore new therapeutic strategies such as combination multi-target therapy (antiviral or double antiviral plus antibody-based therapies) to avoid persistent viral shedding and/or severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: B-cell depleted; MoAbs; antiviral; combined therapy; persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Copyright © 2024 D’Abramo, Vita, Beccacece, Navarra, Pisapia, Fusco, Matusali, Girardi, Maggi, Goletti, Nicastri and ImmunoCOVID team.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . (2023). Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2023-statement-on-the-fifteenth-meet... (Accessed June 12, 2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous