Clustering human dental pulp fibroblasts spontaneously activate NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes and induce IL-1β secretion
- PMID: 38487102
- PMCID: PMC10937208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.02.010
Clustering human dental pulp fibroblasts spontaneously activate NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes and induce IL-1β secretion
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of the present study was to investigate whether NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) and absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasomes pathways were involved in an experimental model of fibroblast activation named nemosis, which was used to mimic circumstances without bacteria stimulation.
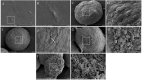
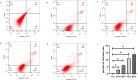
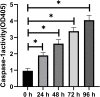
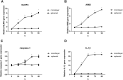
Methods: Nemosis of human dental pulp fibroblast (DPFs) was induced by three-dimensional culture in U-shaped 96-well plates and investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). DPFs monolayers were used as control. Annexin V-FITC/7-AAD apoptosis assay was performed on the DPFs spheroids by flowcytometry. Caspase-1 activity detection assay was conducted on the DPFs spheroids. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), cytokine measurements, Western blot and the effect of COX-2 inhibitor on spheroids was studied.
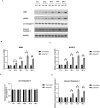
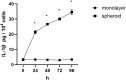
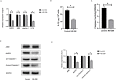
Results: SEM study observed human dental pulp fibroblast clusters and cell membranes damage on the surface of DPFs spheroids. The percentages of necrotic cells from DPFs spheroids gradually increased as the incubation time increased. A statistically significant increase in caspase-1 activity was observed after DPFs spheroids formation. DPFs spheroids displayed significant amounts of NLRP3, AIM2 mRNA and protein expression, caspase-1 mRNA expression and cleaved Caspase-1 protein expression and high IL-1β concentrations (P < 0.05) than DPFs monolayers. Specific COX-2 inhibitor (NS-398) decreased NLRP3 mRNA and protein expression, cleaved Caspase-1 protein expression, Caspase-1 activity and IL-1β mRNA expression and IL-1β concentrations (P < 0.05). However, Specific COX-2 inhibitor had no impact on AIM2 mRNA and protein expression, caspase-1 mRNA expression and pro-Caspase-1 protein expression.
Conclusions: In conclusion, clustering human DPFs spontaneously activated NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes and induced IL-1β secretion which could be partially attenuated by COX-2 inhibitor. Thus, nemosis could become a powerful model for studying mechanisms underlying aseptic pulpitis.
Keywords: Absent in melanoma 2; Dental pulp fibroblast; Inflammasome; Nemosis; Pyrin domain-containing 3.
© 2024 The Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine Secretion and Pyroptosis of Thyroid Follicular Cells Mediated by Enhanced NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4, and AIM2 Inflammasomes Are Associated With Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01197. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915579 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms that lead to the regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome expression and activation in human dental pulp fibroblasts.Mol Immunol. 2015 Aug;66(2):253-62. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25863775
-
Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) in rat dental pulp mediates the inflammatory response during pulpitis.J Endod. 2013 Nov;39(11):1390-4. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Endod. 2013. PMID: 24139260
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
The role of NLRP3 and AIM2 in inflammasome activation during Brucella abortus infection.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Feb;39(2):215-223. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0581-1. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27405866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of acemannan, an extracted product from Aloe vera, on proliferation of dental pulp stem cells and healing of mandibular defects in rabbits.Am J Stem Cells. 2024 Apr 25;13(2):75-86. doi: 10.62347/UAFC3719. eCollection 2024. Am J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 38765804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zero D.T., Zandona A.F., Vail M.M., Spolnik K.J. Dental caries and pulpal disease. Dental Clinics. 2011;55(1):29–46. - PubMed
-
- Bjørndal L., Simon S., Tomson P., Duncan H. Management of deep caries and the exposed pulp. Int Endod J. 2019;52(7):949–973. - PubMed
-
- Zheng J., Wu Z., Niu K., Xie Y., Hu X., Fu J., et al. Microbiome of deep dentinal caries from reversible pulpitis to irreversible pulpitis. J Endod. 2019;45(3):302–309 e1. - PubMed
-
- Vaheri A., Enzerink A., Räsänen K., Salmenperä P. Nemosis, a novel way of fibroblast activation, in inflammation and cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(10):1633–1638. - PubMed
-
- Zhai S., Wang Y., Jiang W., Jia Q., Li J., Wang W., et al. Nemotic human dental pulp fibroblasts promote human dental pulp stem cells migration. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(10):1544–1552. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

