Phenolic phytochemistry, in vitro, in silico, in vivo, and mechanistic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant evaluations of Habenaria digitata
- PMID: 38487169
- PMCID: PMC10937556
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1346526
Phenolic phytochemistry, in vitro, in silico, in vivo, and mechanistic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant evaluations of Habenaria digitata
Abstract
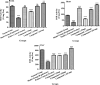
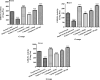
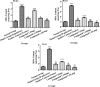
Excessive and imbalance of free radicals within the body lead to inflammation. The objective of the current research work was to explore the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential of the isolated compounds from Habenaria digitata. In this study, the isolated phenolic compounds were investigated for in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory potential along with the antioxidant enzyme. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential of the phenolic compounds was assayed via various enzymes like COX-1/2, 5-LOX and ABTS, DPPH, and H2O2 free radical enzyme inhibitory assay. These compounds were also explored for their in vivo antioxidant activity like examining SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, and MDA levels in the brain, heart, and liver. The anti-inflammatory potential was evaluated using the carrageenan-induced pleurisy model in mice. On the basis of initial screening of isolated compounds, the most potent compound was further evaluated for the anti-inflammatory mechanism. Furthermore, the molecular docking study was also performed for the potent compound. The phenolic compounds were isolated and identified by GC-MS/NMR analysis by comparing its spectra to the library spectra. The isolated phenolic compounds from H. digitata were 5-methylpyrimidine-24,4-diol (1), 3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-2,3-dihydropyran-4-one (2), 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol (3), 3-methoxy-4-vinylphenol (4), and 2,6-dimethoxy-4-vinylphenol (5). In in vitro antioxidant assay, the most potent compound was compound 1 having IC50 values of 0.98, 0.90, and 5 μg/mL against ABTS, DPPH, and H2O2, respectively. Similarly, against COX1/2 and 5-LOX ,compound 1 was again the potent compound with IC50 values of 42.76, 10.70, and 7.40 μg/mL. Based on the in vitro results, compound 1 was further evaluated for in vivo antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential. Findings of the study suggest that H. digitata contains active compounds with potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. These compounds could be screened as drug candidates for pharmaceutical research, targeting conditions associated with oxidative stress and inflammatory conditions in medicinal chemistry and support their ethnomedicinal use for inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: Habenaria digitata; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; mechanism; molecular docking; phenolic.
Copyright © 2024 Almasoudi, Saeed Jan, Nahari, Alhazmi, Binshaya, Abdulaziz, Mahnashi, Ibrar, Zafar and Sadiq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
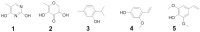





Similar articles
-
Phytochemical profiling of bioactive compounds, anti-inflammatory and analgesic potentials of Habenaria digitata Lindl.: Molecular docking based synergistic effect of the identified compounds.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jun 12;273:113976. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113976. Epub 2021 Feb 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33647424
-
Isolation, invitro, invivo anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antioxidant potential of Habenaria plantegania Lindl.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Apr;32(2):1353-1369. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01425-4. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38334860
-
Evaluation of Habenaria aitchisonii Reichb. for antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antinociceptive effects with in vivo and in silico approaches.Front Chem. 2024 Mar 19;12:1351827. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1351827. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38566899 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential of Guaianolide isolated from Cyathocline purpurea: Role of COX-2 inhibition.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:110-118. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28888779
-
Phytochemical Characterization, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Cleome arabica L. Fruits Extract against Formalin Induced Chronic Inflammation in Female Wistar Rat: Biochemical, Histological, and In Silico Studies.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):26. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010026. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615222 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological evaluation and binding behavior of 4,4'-diamino-2,2'-stilbene disulfonic acid with metal ions using spectroscopic techniques.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 14;10(14):e34639. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34639. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39148976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adwas A. A., Elsayed A., Azab A., Quwaydir F., Ibrahim Elsayed . S. (2019). Oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms in human body. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 6, 43–47. 10.15406/jabb.2019.06.00173 - DOI
-
- Ahmad G., Rasool N., Rizwan K., Imran I., Zahoor A. F., Zubair M., et al. (2019). Synthesis, in-vitro cholinesterase inhibition, in-vivo anticonvulsant activity and in-silico exploration of N-(4-methylpyridin-2-yl) thiophene-2-carboxamide analogs. Bioorg. Chem. 92, 103216. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103216 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alam F., Din K. M., Rasheed R., Sadiq A., Jan M. S., Minhas A. M., et al. (2020). Phytochemical investigation, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and antinociceptive activities of Zanthoxylum armatum DC extracts-in vivo and in vitro experiments. Heliyon 6, e05571. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05571 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alqahtani Y. S., Jan M. S., Mahnashi M. H., Alyami B. A., Alqarni A. O., Rashid U., et al. (2022). Anti-inflammatory potentials of β-ketoester derivatives of N-ary succinimides: in vitro, in vivo, and molecular docking studies. J. Chem. 2022, 1–11. 10.1155/2022/8040322 - DOI
-
- Alshehri O. M., Alshamrani S., Mahnashi M. H., Alshahrani M. M., Khan J. A., Shah M., et al. (2022). Phytochemical analysis, total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and anticancer evaluations of solvent extracts and saponins of H. digitata. BioMed Res. Int., 2022. 10.1007/s10787-023-01425-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

