Novel insight into the therapeutical potential of flavonoids from traditional Chinese medicine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 38487170
- PMCID: PMC10937431
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1352760
Novel insight into the therapeutical potential of flavonoids from traditional Chinese medicine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
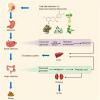
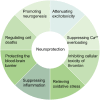
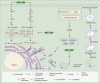
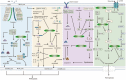
Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (CIRI) is a major contributor to poor prognosis of ischemic stroke. Flavonoids are a broad family of plant polyphenols which are abundant in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and have beneficial effects on several diseases including ischemic stroke. Accumulating studies have indicated that flavonoids derived from herbal TCM are effective in alleviating CIRI after ischemic stroke in vitro or in vivo, and exhibit favourable therapeutical potential. Herein, we systematically review the classification, metabolic absorption, neuroprotective efficacy, and mechanisms of TCM flavonoids against CIRI. The literature suggest that flavonoids exert potential medicinal functions including suppressing excitotoxicity, Ca2+ overloading, oxidative stress, inflammation, thrombin's cellular toxicity, different types of programmed cell deaths, and protecting the blood-brain barrier, as well as promoting neurogenesis in the recovery stage following ischemic stroke. Furthermore, we identified certain matters that should be taken into account in future research, as well as proposed difficulties and opportunities in transforming TCM-derived flavonoids into medications or functional foods for the treatment or prevention of CIRI. Overall, in this review we aim to provide novel ideas for the identification of new prospective medication candidates for the therapeutic strategy against ischemic stroke.
Keywords: cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (CIRI); flavonoid; ischemic stroke; neuroprotection; traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Sun, Zhang, Feng, Yang and Mei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury:a review of the mechanism.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 16;14:1220862. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1220862. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37654609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insight into the Modulatory Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 10;19:185-200. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S500505. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39810832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of SIRTs in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury and targeted intervention of Chinese medicine].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Oct;47(20):5406-5417. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220706.601. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36471954 Review. Chinese.
-
Astrocyte modulation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: A promising therapeutic strategy.Exp Neurol. 2024 Aug;378:114814. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114814. Epub 2024 May 16. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38762094 Review.
-
Therapeutic targets of neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke: Applications for natural compounds from medicinal herbs.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Apr;148:112719. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112719. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35168073 Review.
Cited by
-
Possible opportunities and challenges for traditional Chinese medicine research in 2035.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1426300. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1426300. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38974044 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine in the management of ischemic stroke: a narrative review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1561688. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1561688. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Mechanism of Xinbao Pill in Brain Injury After Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Based on Network Pharmacology, Metabolomics, and Experimental Verification.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Mar;31(3):e70297. doi: 10.1111/cns.70297. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40035287 Free PMC article.
-
Zuogui Pill Promotes Neurovascular Regeneration and Corticospinal Tract Remodeling After Ischemic Stroke.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 21;19:4221-4243. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S518696. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40416793 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction and purification of total flavonoids from Zanthoxylum planispinum Var. Dintanensis leaves and effect of altitude on total flavonoids content.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 27;15(1):7080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91528-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40016497 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

