A comprehensive evaluation of the therapeutic potential of silibinin: a ray of hope in cancer treatment
- PMID: 38487172
- PMCID: PMC10937417
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1349745
A comprehensive evaluation of the therapeutic potential of silibinin: a ray of hope in cancer treatment
Abstract
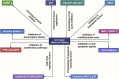
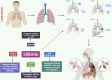
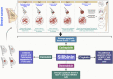
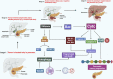
Natural compounds hold promise in the search for cancer therapies due to their unique chemical structures and combinations that may effectively combat cancer while minimizing toxicity and side effects compared to conventional treatments. Silibinin, a natural lignan, has been found to possess strong anti-cancer activity against several types of human cancers based on emerging research. This study aims to provide an overview of the therapeutic potential of silibinin in the treatment and prevention of cancers. A comprehensive search was conducted using various internet databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect to identify relevant research papers. Silibinin has been shown to exhibit anticancer activity against several types of cancers, including liver, lungs, breast, prostate, colorectal, skin, and bladder cancers. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action contribute to its therapeutic effects. Silibinin exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic, anti-metastatic, and anti-angiogenic activities, making it a promising candidate for cancer therapy. One of the key mechanisms underlying the anticancer effects of silibinin is its ability to modulate multiple signaling pathways involved in cancer development and progression. It can inhibit the activation of various oncogenic pathways, including PI3K/Akt, NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin, and MAPK pathways, thereby suppressing cancer cell proliferation, inducing cell cycle arrest, and promoting apoptosis. Silibinin possesses great potential as an effective treatment agent for cancer. The multifaceted mechanisms of action, favorable safety profile, and potential synergistic effects of silibinin with conventional therapies make it an attractive candidate for further investigation and development as a cancer treatment. However, more extensive clinical studies are necessary to fully establish the efficacy, optimal dosage, and long-term effects of silibinin in cancer treatment.
Keywords: anti-angiogenic; anti-inflammatory; anti-metastatic; anti-proliferative; antioxidant; apoptosis; cancer; silibinin.
Copyright © 2024 Ray, Islam, Islam, Han, Geng, Aziz and Mamun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Berthold D. R., Pond G. R., Roessner M., De Wit R., Eisenberger M., Tannock I. F., et al. (2008). Treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer with docetaxel or mitoxantrone: relationships between prostate-specific antigen, pain, and quality of life response and survival in the TAX-327 study. Clin. Cancer Res. 14 (9), 2763–2767. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0944 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhatia N., Agarwal C., Agarwal R. (2001). Differential responses of skin cancer-chemo preventive agents silibinin, quercetin, and epigallocatechin 3-gallate on mitogenic signaling and cell cycle regulators in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Nutr. cancer 39 (2), 292–299. 10.1207/S15327914nc392_20 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Binienda A., Ziolkowska S., Pluciennik E. (2020). The anticancer properties of silibinin: its molecular mechanism and therapeutic effect in breast cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. Former. Curr. Med. Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents 20 (15), 1787–1796. 10.2174/1871520620666191220142741 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang H. R., Chen P. N., Yang S. F., Sun Y. S., Wu S. W., Hung T. W., et al. (2011). Silibinin inhibits the invasion and migration of renal carcinoma 786-O cells in vitro, inhibits the growth of xenografts in vivo and enhances chemosensitivity to 5‐fluorouracil and paclitaxel. Mol. Carcinog. 50 (10), 811–823. 10.1002/mc.20756 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

