Effects of Taekkyon-based exercise program on balance, lower extremity strength, and gait parameters in community-dwelling older women: Randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38489715
- PMCID: PMC10939652
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037463
Effects of Taekkyon-based exercise program on balance, lower extremity strength, and gait parameters in community-dwelling older women: Randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: As individuals age, they experience a decline in muscle strength and balance, leading to diminished functional capacity and an increased risk of falls. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the effects of the Taekkyon-based exercise program on balance, muscle strength, and gait ability in women aged over 65-year-old residing in the local community.
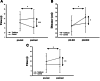
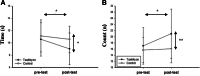
Methods: Forty-eight subjects were randomly allocated into the Taekkyon-based exercise program as an experimental group (EG = 25; mean age: 71.68 ± 3.26) or a fall prevention program as a control group (CG = 23; mean age: 73.65 ± 5.88). EG participants received 1-hour Taekkyon exercise sessions twice a week for 12 consecutive weeks. CG participants received a typical fall prevention program. The measurements in each group included assessments of balance levels (the timed up-and-go test, one-leg stance, and functional reach test), lower extremity strength (the 5-chair stand test and 30-second chair stand test), and gait parameters (cadence, step length, step width, stride length, stride time, and gait velocity) before and after the intervention.
Results: After the intervention, balance (timed up-and-go test, one-leg stance, and functional reach test), lower extremity strength (5-chair stand test and 30-second chair stand test), and gait parameters (cadence, stride time, and gait velocity) showed a significant improvement in EG participants compared to CG participants (P < .05). Compared to the normal value of balance ability and strength of elderly women over 65 years of age, most outcomes were greater than average normal values for those receiving Taekkyon exercise.
Conclusion: Taekkyon-based exercise program was more effective in improving balance, lower extremity strength, and gait capacity than the usual fall prevention program in elderly women over 65 years of age. Its effects can approach normal values for women in this age group. The 12-week Taekkyon-based exercise program could be useful as part of a fall prevention program to elderly people.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Tai Chi versus Taekkyon on balance, lower-extremity strength, and gait ability in community-dwelling older women: A single-blinded randomized clinical trial.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020;33(1):41-48. doi: 10.3233/BMR-181493. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 31282402 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of 2 Different Exercise Approaches: Tai Chi Versus Otago, in Community-Dwelling Older Women.J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2016 Apr-Jun;39(2):51-7. doi: 10.1519/JPT.0000000000000042. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2016. PMID: 25760277 Clinical Trial.
-
A best practice fall prevention exercise program to improve balance, strength / power, and psychosocial health in older adults: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.BMC Geriatr. 2013 Oct 9;13:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-13-105. BMC Geriatr. 2013. PMID: 24106864 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 31;1(1):CD012424. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012424.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30703272 Free PMC article.
-
Association of lower-limb strength with different fall histories or prospective falls in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Feb 6;25(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-05685-3. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 39915768 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Taekwondo intervention on balance ability: A meta-analysis and systematic review.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 13;20(2):e0317844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317844. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39946326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lieber RL. Skeletal Muscle Structure, Function, and Plasticity. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002.
-
- Judge JO, Lindsey C, Underwood M, et al. . Balance improvements in older women: effects of exercise training. Phys Ther. 1993;73:254–62; discussion 263. - PubMed
-
- Carter ND, Khan KM, Mallinson A, et al. . Knee extension strength is a significant determinant of static and dynamic balance as well as quality of life in older community-dwelling women with osteoporosis. Gerontology. 2002;48:360–8. - PubMed
-
- Lord SR, Castell S. Physical activity program for older persons: effect on balance, strength, neuromuscular control, and reaction time. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994;75:648–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

