Prevalence, outcomes and associated factors of SARS-CoV-2 infection in psoriasis patients of Southwest China: a cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 38491005
- PMCID: PMC10943245
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54424-y
Prevalence, outcomes and associated factors of SARS-CoV-2 infection in psoriasis patients of Southwest China: a cross-sectional survey
Abstract
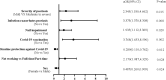
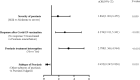
In this study we aimed to investigate the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in psoriasis patients, and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection and associated risk factors. A cross-sectional survey was conducted from February 2023 to March 2023. Information was obtained with online questionnaire about psoriasis patients on demographic characteristics, clinical characteristics, SARS-CoV-2 infection and outcomes, vaccination, and routine protection against COVID-19. Logistic regression analysis was used to explore risk factors with SARS-CoV-2 infection and exacerbation of psoriasis. A total of 613 participants were recruited. 516 (84.2%) were infected, and associated factors were sex, working status, routine protection against COVID-19, COVID-19 vaccination, impaired nail, infection exacerbate psoriasis, and severity of psoriasis. Among the patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, 30 (5.8%) required hospitalization, 122 (23.6%) had psoriasis exacerbation due to SARS-CoV-2 infection, and associated factors were subtype of psoriasis, discontinuation of psoriasis treatment during SARS-CoV-2 infection, response following COVID-19 vaccination, and severity of psoriasis. Booster dose vaccination contributed a low probability of COVID-19 sequelae. COVID-19 vaccine's effectiveness was unsatisfactory, while booster dose vaccination reduced the occurrence of COVID-19 sequelae in psoriasis patients of Southwest China. Patients treated with psoriasis shown to be safe, without a higher incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19hospitalization compared to untreated patients. Stopping treatment during SARS-CoV-2 infection led to psoriasis exacerbation, so psoriasis treatment could be continued except severe adverse reaction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Hospitalization, and Associated Factors Among People Living With HIV in Southeastern China From December 2022 to February 2023: Cross-Sectional Survey.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Apr 17;10:e51449. doi: 10.2196/51449. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 38630534 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, risk and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections in psoriasis patients receiving conventional systemic, biologic or topical treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional cohort study (PsoCOVID).J Dermatolog Treat. 2023 Dec;34(1):2161297. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2022.2161297. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023. PMID: 36545844
-
Effectiveness of booster vaccination with inactivated COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 infection in Guangdong, China: a cohort study.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 17;14:1257360. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1257360. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37915583 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of the first dose COVID-19 booster vs. full vaccination to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 clinical event: a meta-analysis and systematic review of longitudinal studies.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 1;11:1165611. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1165611. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37325336 Free PMC article.
-
Use of biologics during the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons learned from psoriasis.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022 Dec;22(12):1521-1529. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2022.2110467. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35930356 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between body roundness index and psoriasis: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 28;15(1):10796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91814-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40155396 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025 Jun 26;11(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s41572-025-00630-5. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025. PMID: 40571687 Review.
References
-
- Notice on further optimization of the implementation of measures for the prevention and control of the COVID-19 epidemic. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-12/07/content_5730443.htm (last accessed: 7 December 2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

