HYADES - A Global Archive of Annual Maxima Daily Precipitation
- PMID: 38491034
- PMCID: PMC10943004
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03109-2
HYADES - A Global Archive of Annual Maxima Daily Precipitation
Abstract
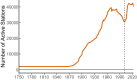
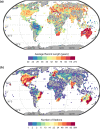
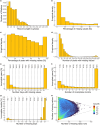
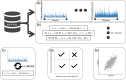
Time series of annual maxima daily precipitation are crucial for understanding extreme precipitation behavior and its shifts toward nonstationarity with global warming. Extreme precipitation insight assists hydraulic infrastructure design, water resource management, natural hazard prevention, and climate change adaptation. However, not even a third of the records are of sufficient length, and the number of active stations keeps decreasing. Herein, we present HYADES: archive of yearly maxima of daily precipitation records, a global dataset derived from the Global Historical Climatology Network database of daily records (GHCN-Daily). The HYADES dataset contains records from 39 206 stations (heterogeneously distributed worldwide) with record lengths varying from 16 to 200 years between 1805 and 2023. HYADES was extracted through a methodology designed to accurately capture the true maxima even in the presence of missing values within the records. The method's thresholds were determined and evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations. Our approach demonstrates a 96.73% success rate in detecting the true maxima while preserving time series statistical properties of interest (L-moments and temporal monotonic trend).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Global Historical Climatology Network Monthly Precipitation Dataset, Version 4.Sci Data. 2024 Jun 15;11(1):633. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03457-z. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38879587 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal trends in mean and extreme climate variables over 1981-2020 in Meki watershed of central rift valley basin, Ethiopia.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 19;8(11):e11684. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11684. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36439755 Free PMC article.
-
Variation characteristics of extreme climate events in Southwest China from 1961 to 2017.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 30;9(9):e19648. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19648. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809861 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of climate change on precipitation and discharge extremes through the use of statistical downscaling approaches in a Mediterranean basin.Sci Total Environ. 2016 Feb 1;543(Pt B):952-64. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.088. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Sci Total Environ. 2016. PMID: 26146163
-
[Changes of China agricultural climate resources under the background of global climate change. VI. Change characteristics of precipitation resource and its possible effect on maize production in Sanjiang Plain of Heilongjiang Province].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2011 Jun;22(6):1511-22. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21941753 Chinese.
References
-
- Trenberth, K. E., Dai, A., Rasmussen, R. M. & Parsons, D. B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society84, 1205–1218, 10.1175/BAMS-84-9-1205 (2003).
-
- AghaKouchak A, et al. Climate Extremes and Compound Hazards in a Warming World. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 2020;48:519–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-071719-055228. - DOI
-
- Min, S.-K., Zhang, X., Zwiers, F. W. & Hegerl, G. C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature470, 378–381, 10.1038/nature09763 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Haque U, et al. Fatal landslides in Europe. Landslides. 2016;13:1545–1554. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0689-3. - DOI
-
- Mallakpour I, AghaKouchak A, Sadegh M. Climate-Induced Changes in the Risk of Hydrological Failure of Major Dams in California. Geophysical Research Letters. 2019;46:2130–2139. doi: 10.1029/2018GL081888. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

