Prognostic factors of renal cell cancer in elderly patients: a population-based cohort study
- PMID: 38491173
- PMCID: PMC10942969
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-56835-3
Prognostic factors of renal cell cancer in elderly patients: a population-based cohort study
Abstract
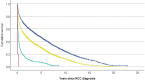
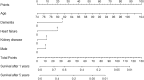
Mortality in renal cell cancer (RCC) is high in the elderly population. Comorbidities have a greater impact on overall prognosis of RCC among elderly patients than in younger patients. All new RCC cases were collected in people over 74 years of age between 1995 and 2018 from the Finnish cancer registry. The comorbidities were identified from the Care Registry for Healthcare. Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) was used to evaluate the risk of death based on comorbidities. The overall risk of death was analyzed using the Cox regression model. The risk for RCC death was analyzed using Fine and Gray regression analysis. Individual prognostic role of CCI components was evaluated by adding each component separately into the multivariable Fine and Gray regression model. Using the most prognostic comorbidities we constructed a nomogram to predict RCC mortality. Statistically significant prognostic factors of RCC death were tumor morphology (clear cell, papillary and chromophobe), sex, operative treatment, age, primary tumor extent and CCI. The strongest prognostic factors for overall mortality were tumor extent, tumor morphology and operative treatment. Among the components of CCI, the most important comorbidities predicting mortality were dementia, heart failure and kidney disease. The limitation of this study is that the comorbidities have only been recorded at inpatient and outpatient hospital contacts, which is why the prevalence of comorbidities is probably underestimated. In addition, physical performance status was not available from registry data, but it significantly affects the treatment decisions. RCC mortality is high in the elderly population. Among comorbidities, dementia and heart failure have the greatest impact on the prognosis. Curative treatment in selected elderly patients is efficient and should be considered in patients who can tolerate it and have only limited comorbidities.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of comorbidity on risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with renal cell carcinoma.Urol Oncol. 2014 May;32(4):466-72. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.07.008. Urol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24767684 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating overall survival and competing risks of death in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma using a comprehensive nomogram.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jan 10;28(2):311-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.4816. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19933918 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Advanced Age in Patients with T1a Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated by Microwave Ablation: A 16-Year Experience.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231183585. doi: 10.1177/15330338231183585. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 38018134 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome prediction for renal cell carcinoma: evaluation of prognostic factors for tumours divided according to histological subtype.Pathology. 2007 Oct;39(5):459-65. doi: 10.1080/00313020701570061. Pathology. 2007. PMID: 17886093 Review.
-
Nephron-sparing surgery for renal cell carcinoma: clinicopathologic features predictive of patient outcome.Urology. 2003 Oct;62(4):641-6. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(03)00489-8. Urology. 2003. PMID: 14550434 Review.
Cited by
-
Up-regulation of Cuproptosis-related lncRNAS in Patients Receiving Immunotherapy for Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Indicates Progressive Disease.In Vivo. 2025 Jan-Feb;39(1):146-151. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13812. In Vivo. 2025. PMID: 39740865 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for localized renal masses in elderly and younger patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes.World J Urol. 2025 May 29;43(1):335. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05712-3. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40439733 Review.
-
Real-world comparison of the efficacy of first-line therapies and the influence of risk factors in advanced renal cell carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 19;16(1):359. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02131-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40106049 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the evolving landscape of kidney cancer mortality in the United States.Oncologist. 2025 Apr 4;30(4):oyae373. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae373. Oncologist. 2025. PMID: 40304256 Free PMC article.
-
Competing risk of death in patients with low, intermediate and high risk of recurrence after radical surgery for clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BJUI Compass. 2025 Jul 21;6(7):e70047. doi: 10.1002/bco2.70047. eCollection 2025 Jul. BJUI Compass. 2025. PMID: 40698356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- EAU-Guidelines-on-Renal-Cell-Carcinoma-2021.pdf.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

