MemPrep, a new technology for isolating organellar membranes provides fingerprints of lipid bilayer stress
- PMID: 38491296
- PMCID: PMC11021466
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00063-y
MemPrep, a new technology for isolating organellar membranes provides fingerprints of lipid bilayer stress
Abstract
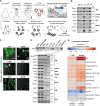
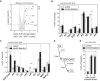
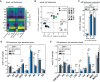
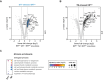
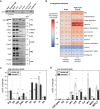
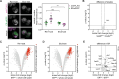
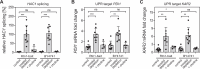
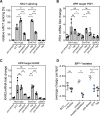
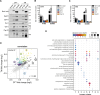
Biological membranes have a stunning ability to adapt their composition in response to physiological stress and metabolic challenges. Little is known how such perturbations affect individual organelles in eukaryotic cells. Pioneering work has provided insights into the subcellular distribution of lipids in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, but the composition of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, which also crucially regulates lipid metabolism and the unfolded protein response, remains insufficiently characterized. Here, we describe a method for purifying organelle membranes from yeast, MemPrep. We demonstrate the purity of our ER membrane preparations by proteomics, and document the general utility of MemPrep by isolating vacuolar membranes. Quantitative lipidomics establishes the lipid composition of the ER and the vacuolar membrane. Our findings provide a baseline for studying membrane protein biogenesis and have important implications for understanding the role of lipids in regulating the unfolded protein response (UPR). The combined preparative and analytical MemPrep approach uncovers dynamic remodeling of ER membranes in stressed cells and establishes distinct molecular fingerprints of lipid bilayer stress.
Keywords: ER Stress; Lipid Bilayer Stress; MemPrep; Organelle Lipidomics; UPR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CK declares competing financial interests related to the publication of this study, including being chief technology officer at Lipotype GmbH, Dresden. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

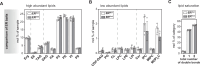
References
-
- Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, Van Gunsteren WF, Dinola A, Haak JR. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys. 1984;81:3684–3690. doi: 10.1063/1.448118. - DOI
-
- Best RB, Zhu X, Shim J, Lopes PEM, Mittal J, Feig M, Mackerell AD. Optimization of the additive CHARMM all-atom protein force field targeting improved sampling of the backbone φ, ψ and side-chain χ(1) and χ(2) dihedral angles. J Chem Theory Comput. 2012;8:3257–3273. doi: 10.1021/ct300400x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

