Affinity fine-tuning anti-CAIX CAR-T cells mitigate on-target off-tumor side effects
- PMID: 38491381
- PMCID: PMC10943873
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-01952-w
Affinity fine-tuning anti-CAIX CAR-T cells mitigate on-target off-tumor side effects
Abstract
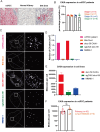
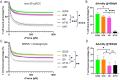
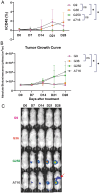
One of the major hurdles that has hindered the success of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies against solid tumors is on-target off-tumor (OTOT) toxicity due to sharing of the same epitopes on normal tissues. To elevate the safety profile of CAR-T cells, an affinity/avidity fine-tuned CAR was designed enabling CAR-T cell activation only in the presence of a highly expressed tumor associated antigen (TAA) but not when recognizing the same antigen at a physiological level on healthy cells. Using direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) which provides single-molecule resolution, and flow cytometry, we identified high carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) density on clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) patient samples and low-density expression on healthy bile duct tissues. A Tet-On doxycycline-inducible CAIX expressing cell line was established to mimic various CAIX densities, providing coverage from CAIX-high skrc-59 tumor cells to CAIX-low MMNK-1 cholangiocytes. Assessing the killing of CAR-T cells, we demonstrated that low-affinity/high-avidity fine-tuned G9 CAR-T has a wider therapeutic window compared to high-affinity/high-avidity G250 that was used in the first anti-CAIX CAR-T clinical trial but displayed serious OTOT effects. To assess the therapeutic effect of G9 on patient samples, we generated ccRCC patient derived organotypic tumor spheroid (PDOTS) ex vivo cultures and demonstrated that G9 CAR-T cells exhibited superior efficacy, migration and cytokine release in these miniature tumors. Moreover, in an RCC orthotopic mouse model, G9 CAR-T cells showed enhanced tumor control compared to G250. In summary, G9 has successfully mitigated OTOT side effects and in doing so has made CAIX a druggable immunotherapeutic target.
Keywords: Affinity/avidity fine-tuned; Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX); Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T; Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); Direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM); On-target off-tumor (OTOT) toxicity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
W.A.M has patents in the PD-1/ PDL1 field. G.J.F has patents/pending royalties on the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway from Roche, Merck MSD, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Merck KGA, Boehringer-Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Dako, Leica, Mayo Clinic, Eli Lilly, and Novartis. G.J.F has served on advisory boards for Roche, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Xios, Origimed, Triursus, iTeos, NextPoint, IgM, Jubilant, Trillium, IOME, GV20, Invaria, and Geode. G.J.F has equity in Nextpoint, Triursus, Xios, iTeos, IgM, GV20, Invaria, and Geode. S. S. reports receiving commercial research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Exelixis and Novartis; is a consultant/advisory board member for Merck, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRISPR Therapeutics AG, AACR, and NCI; receives royalties from Biogenex; and mentored several non-US citizens on research projects with potential funding (in part) from non-US sources/Foreign Components. T.K.C. institutional and personal, paid and unpaid support for research, advisory boards, consultancy, and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Aravive, Aveo, Bayer, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Calithera, Circle Pharma, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVA, Infinity, Ipsen, Jansen, Kanaph, Lilly, Merck, Nikang, Nuscan, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Aventis, Surface Oncology, Takeda, Tempest, Up-To-Date, CME events (Peerview, OncLive, MJH and others), outside the submitted work. T.K.C. has institutional patents filed on molecular alterations and immunotherapy response/toxicity, and ctDNA. T.K.C. has equity in Tempest, Pionyr, Osel, Precede Bio. T.K.C. has served on committees for NCCN, GU Steering Committee, ASCO/ESMO, ACCRU, KidneyCan. T.K.C. has medical writing and editorial assistance support may have been funded by Communications companies in part. T.K.C. has mentored several non-US citizens on research projects with potential funding (in part) from non-US sources/Foreign Components. The institution (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute) may have received additional independent funding of drug companies or/and royalties potentially involved in research around the subject matter. C.P.P. is a consultant for XSphera Biosciences and has stock and other ownership interests in XSphera Biosciences. Received honoraria from Thermo Fisher and Agilent and has sponsored research agreements with Daiichi Sankyo, Bicycle Therapeutics, Transcenta, Bicara Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Array Biopharma, Takeda Onkology, Bristol Meyers Squibb, TargImmune, and Mirati Therapeutics. D.A.B. is a consultant for N of One/Qiagen and Nerviano Medical Sciences, is a founder and shareholder in XSphera Biosciences, has received honoraria from Merck, H3 Biomedicine/Esai, EMD Serono, Gilead Sciences, Abbvie, and Madalon Consulting, and research grants from BMS, Takeda, Novartis, Gilead, and Lilly.
Figures



References
-
- First-Ever CAR T-cell Therapy Approved in U.S. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(10):OF1. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28887358/#:~:text=The%20first%20chimeric.... - PubMed
-
- Feng K, Guo Y, Dai H, Wang Y, Li X, Jia H, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the immunotherapy of patients with EGFR-expressing advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Science China Life Sciences. 2016 2016/05/01;59:468–79. 10.1007/s11427-016-5023-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

