Characterizing reference genes for high-fidelity gene expression analysis under different abiotic stresses and elicitor treatments in fenugreek leaves
- PMID: 38491388
- PMCID: PMC10943880
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-024-01167-6
Characterizing reference genes for high-fidelity gene expression analysis under different abiotic stresses and elicitor treatments in fenugreek leaves
Abstract
Background: Quantifying gene expression is a critical aspect of applied genomics research across all organisms, and real-time PCR has emerged as a powerful tool for this purpose. However, selecting appropriate internal control genes for data normalization presents specific challenges. This study aimed to identify suitable reference genes for gene expression analysis under various conditions, encompassing salinity, low and high-temperature stresses, and different elicitor treatments. These treatments included titanium dioxide, cold plasma, 24-epibrassinolide, and melatonin, resulting in a total of 13 unique treatments and 148 treatment combinations applied to fenugreek plants.
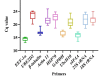
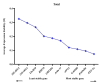
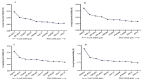
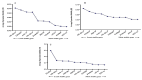
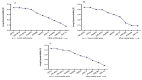
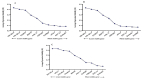
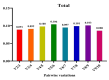
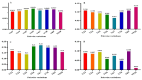
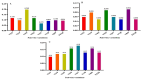
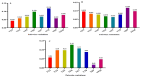
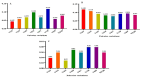
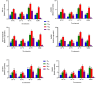
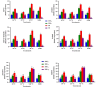
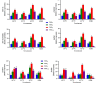
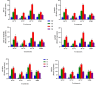
Results: As per the analysis performed with the BestKeeper tool, EEF-1α, and GAPDH were recognized as the most stable reference genes under the majority of conditions. Furthermore, the GeNorm and NormFinder tools identified β-tubulin and EEF-1α as the most stable reference genes. The findings of this research demonstrated that, although the stability of three reference genes expression was acceptable in almost all evaluated treatments, fluctuations in their expression were observed under the treatments of cold stress with TiO2 NPs application, cold plasma application with salinity stress, and cold plasma application with high-temperature stress compared to others. Simultaneously, the GeNorm analysis results demonstrated that in the mentioned treatments, relying on only one reference gene is inadequate. To corroborate the results, we examined the expression profile of the SSR gene, a pivotal gene in diosgenin biosynthesis, under all investigated treatments and treatment combinations. The outcomes suggested that employing stable reference genes yielded highly consistent results.
Conclusions: The varying expression patterns of the target genes emphasize the crucial need for precise optimization of experimental conditions and selecting stable reference genes to achieve accurate results in gene expression studies utilizing real-time PCR. These findings offer valuable insights into the selection of appropriate reference genes for gene expression analysis under diverse conditions using real-time PCR.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; Elicitors; Fenugreek; Housekeeping gene; Real-time PCR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in creeping bentgrass involved in four abiotic stresses.Plant Cell Rep. 2015 Oct;34(10):1825-34. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1830-9. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Plant Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26179072
-
Selection and validation of reference genes for target gene analysis with quantitative RT-PCR in leaves and roots of bermudagrass under four different abiotic stresses.Physiol Plant. 2015 Oct;155(2):138-148. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12302. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Physiol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25331743
-
Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of Nitraria sibirica under various abiotic stresses.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Dec 17;22(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03988-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36526980 Free PMC article.
-
Reference gene selection for qRT-PCR analyses of luffa (Luffa cylindrica) plants under abiotic stress conditions.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 4;11(1):3161. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81524-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33542253 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and evaluation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in Polygonum cuspidatum based on transcriptome data.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Nov 14;19(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2108-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31726985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alemayehu D. Application of Genetic Engineering in Plant Breeding for biotic stress resistance. Int J Res Stud Biosci (IJRSB) 2017;5(9):28–35.
-
- Zhou P, Huang L, Wang Y, Li X, Feng X, Li L. Stepwise optimization of the RT-qPCR protocol and the evaluation of housekeeping genes in Pears (Pyrus Bretschneideri) under various hormone treatments and stresses. Horticulturae. 2023;9:275. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae9020275. - DOI
-
- Mohamadi Esboei M, Ebrahimi A, Amerian MR, Alipour H. Melatonin confers fenugreek tolerance to salinity stress by stimulating the biosynthesis processes of enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content. Font Plant Sci. 2022;13:890613. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.890613. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

