Using new indices to predict metabolism dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): analysis of the national health and nutrition examination survey database
- PMID: 38491451
- PMCID: PMC10943835
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03190-2
Using new indices to predict metabolism dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): analysis of the national health and nutrition examination survey database
Abstract
Background: Metabolism dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is the most common chronic liver disease. Few MAFLD predictions are simple and accurate. We examined the predictive performance of the albumin-to-glutamyl transpeptidase ratio (AGTR), plasma atherogenicity index (AIP), and serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (UHR) for MAFLD to design practical, inexpensive, and reliable models.
Methods: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007-2016 cycle dataset, which contained 12,654 participants, was filtered and randomly separated into internal validation and training sets. This study examined the relationships of the AGTR and AIP with MAFLD using binary multifactor logistic regression. We then created a MAFLD predictive model using the training dataset and validated the predictive model performance with the 2017-2018 NHANES and internal datasets.
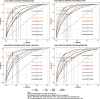
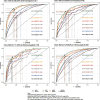
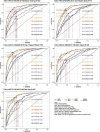
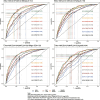
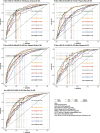
Results: In the total population, the predictive ability (AUC) of the AIP, AGTR, UHR, and the combination of all three for MAFLD showed in the following order: 0.749, 0.773, 0.728 and 0.824. Further subgroup analysis showed that the AGTR (AUC1 = 0.796; AUC2 = 0.690) and the combination of the three measures (AUC1 = 0.863; AUC2 = 0.766) better predicted MAFLD in nondiabetic patients. Joint prediction outperformed the individual measures in predicting MAFLD in the subgroups. Additionally, the model better predicted female MAFLD. Adding waist circumference and or BMI to this model improves predictive performance.
Conclusion: Our study showed that the AGTR, AIP, and UHR had strong MAFLD predictive value, and their combination can increase MAFLD predictive performance. They also performed better in females.
Keywords: AIP; ALB/GGT; Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver; NHANES; Predictive models; UHR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association of serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with cardiovascular disease risk in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional NHANES analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 9;12:1561594. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1561594. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40271428 Free PMC article.
-
Atherogenic index of plasma combined with waist circumference and body mass index to predict metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 28;28(36):5364-5379. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i36.5364. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36185625 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and Analysis of Risk Prediction Model for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Physical Examination Population].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May;54(3):591-595. doi: 10.12182/20230560109. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37248589 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Validation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) related steatosis indices in metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and comparison of the diagnostic accuracy between NAFLD and MAFLD.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Apr 1;35(4):394-401. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002497. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36695773 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a new nomogram to screen for MAFLD.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Dec 8;21(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01748-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36482400 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of wrist circumference with metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease in the KADEM cohort.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 7;16:1580209. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1580209. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40852186 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with cardiovascular disease risk in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional NHANES analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 9;12:1561594. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1561594. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40271428 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based identification of biochemical markers to predict hepatic steatosis in patients at high metabolic risk.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 21;31(27):108200. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108200. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40741101 Free PMC article.
-
Serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio predicts all-cause mortality in adults with metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 2;15(1):11278. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94651-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40175515 Free PMC article.
-
The serum uric acid to apolipoprotein A1 ratio is independently correlated with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: findings from a single national metabolic management center cohort.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 4;16:1619003. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1619003. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40535329 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

