Three complete chloroplast genomes from two north American Rhus species and phylogenomics of Anacardiaceae
- PMID: 38491489
- PMCID: PMC10943888
- DOI: 10.1186/s12863-024-01200-6
Three complete chloroplast genomes from two north American Rhus species and phylogenomics of Anacardiaceae
Abstract
Background: The suamc genus Rhus (sensu stricto) includes two subgenera, Lobadium (ca. 25 spp.) and Rhus (ca. 10 spp.). Their members, R. glabra and R. typhina (Rosanae: Sapindales: Anacardiaceae), are two economic important species. Chloroplast genome information is of great significance for the study of plant phylogeny and taxonomy.
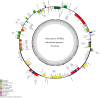
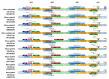
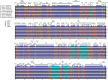
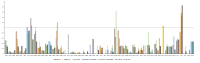
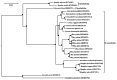
Results: The three complete chloroplast genomes from two Rhus glabra and one R. typhina accessions were obtained with a total of each about 159k bp in length including a large single-copy region (LSC, about 88k bp), a small single-copy regions (SSC, about 19k bp) and a pair of inverted repeats regions (IRa/IRb, about 26k bp), to form a canonical quadripartite structure. Each genome contained 88 protein-coding genes, 37 transfer RNA genes, eight ribosomal RNA genes and two pseudogenes. The overall GC content of the three genomes all were same (37.8%), and RSCU values showed that they all had the same codon prefers, i.e., to use codon ended with A/U (93%) except termination codon. Three variable hotspots, i.e., ycf4-cemA, ndhF-rpl32-trnL and ccsA-ndhD, and a total of 152-156 simple sequence repeats (SSR) were identified. The nonsynonymous (Ka)/synonymous (Ks) ratio was calculated, and cemA and ycf2 genes are important indicators of gene evolution. The phylogenetic analyses of the family Anacardiaceae showed that the eight genera were grouped into three clusters, and supported the monophyly of the subfamilies and all the genera. The accessions of five Rhus species formed four clusters, while, one individual of R. typhina grouped with the R. glabra accessions instead of clustering into the two other individuals of R. typhina in the subgenus Rhus, which showed a paraphyletic relationship.
Conclusions: Comparing the complete chloroplast genomes of the Rhus species, it was found that most SSRs were A/T rich and located in the intergenic spacer, and the nucleotide divergence exhibited higher levels in the non-coding region than in the coding region. The Ka/Ks ratio of cemA gene was > 1 for species collected in America, while it was < 1 for other species in China, which dedicated that the Rhus species from North America and East Asia have different evolutionary pressure. The phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genome clarified the Rhus placement and relationship. The results obtained in this study are expected to provide valuable genetic resources to perform species identification, molecular breeding, and intraspecific diversity of the Rhus species.
Keywords: Rhus; Chloroplast phylogenomics; Genome sequencing; Sumac.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of 18 chloroplast genomes reveals genomic diversity and evolutionary dynamics in subtribe Malaxidinae (Orchidaceae).BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 2;25(1):1013. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06772-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40753185 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into chloroplast genome structure and phylogenetic position of the Lacquer tree Toxicodendron trichocarpum (Anacardiaceae: Rhoideae).J Plant Res. 2025 Jul 27. doi: 10.1007/s10265-025-01661-5. Online ahead of print. J Plant Res. 2025. PMID: 40715651
-
Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Lithocarpus Species (Fagaceae) in South China.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 22;16(6):616. doi: 10.3390/genes16060616. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565508 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
-
- Muellner-Riehl AN, Weeks A, Clayton JW, Buerki S, Nauheimer L, Chiang Y, Cody S, Pell SK. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular clock dating of Sapindales based on plastid rbcL, atpB and trnL-trnF. DNA Sequences Taxon. 2016;65(18):1019–36. doi: 10.12705/655.5. - DOI
-
- Pell SK. Molecular systematics of the cashew family (Anacardiaceae) La State Univ. 2004 doi: 10.31390/gradschool_dissertations.1472. - DOI
-
- Pell SK, Mitchell JD, Miller AJ et al. Anacardiaceae. In Kubitzki, K, editor, The families and genera of vascular plants. Flowering plants. Eudicots. Sapindales, Cucurbitales, Myrtaceae. (Springer-Verlag: Berlin). 2011; 10: 7–50.
-
- Miller AJ, Young DA, Wen J. Phylogeny and biogeography of Rhus (Anacardiaceae) based on its sequence data. Int J Plant Sci. 2001;162:1401–7. doi: 10.1086/322948. - DOI
-
- Lee WK, Kim MJ, Heo K. Phylogeny of Korean Rhus spp. based on ITS and rbcL sequences. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;12:60–66.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
