Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Analysis of Alliance A021501: Preoperative mFOLFIRINOX or mFOLFIRINOX Plus Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy for Borderline Resectable Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas
- PMID: 38492812
- PMCID: PMC11329353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.03.013
Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Analysis of Alliance A021501: Preoperative mFOLFIRINOX or mFOLFIRINOX Plus Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy for Borderline Resectable Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas
Abstract
Purpose: Alliance A021501 is the first randomized trial to evaluate stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In this post hoc study, we reviewed the quality of radiation therapy (RT) delivered.
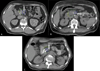
Methods and materials: SBRT (6.6 Gy × 5) was intended but hypofractionated RT (5 Gy × 5) was permitted if SBRT specifications could not be met. Institutional credentialing through the National Cancer Institute-funded Imaging and Radiation Oncology Core (IROC) was required. Rigorous RT quality assurance (RT QA) was mandated, including pretreatment review by a radiation oncologist. Revisions were required for unacceptable deviations. Additionally, we performed a post hoc RT QA analysis in which contours and plans were reviewed by 3 radiation oncologists and assigned a score (1, 2, or 3) based on adequacy. A score of 1 indicated no deviation, 2 indicated minor deviation, and 3 indicated a major deviation that could be clinically significant. Clinical outcomes were compared by treatment modality and by case score.
Results: Forty patients were registered to receive RT (1 planned but not treated) at 27 centers (18 academic and 9 community). Twenty-three centers were appropriately credentialed for moving lung/liver targets and 4 for static head and neck only. Thirty-two of 39 patients (82.1%) were treated with SBRT and 7 (17.9%) with hypofractionated RT. Five cases (13%) required revision before treatment. On post hoc review, 23 patients (59.0%) were noted to have suboptimal contours or plan coverage, 12 (30.8%) were scored a 2, and 11 (28.2%) were scored a 3. There were no apparent differences in failure patterns or surgical outcomes based on treatment technique or post hoc case score. Details related to on-treatment imaging were not recorded.
Conclusions: Despite rigorous QA, we encountered variability in simulation, contouring, plan coverage, and dose on trial. Although clinical outcomes did not appear to have been affected, findings from this analysis serve to inform subsequent PDAC SBRT trial designs and QA requirements.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
MC has received grant funding from ViewRay and StrataPharma (to institution), consulting fees from ViewRay, payment/honoraria from ViewRay, University of Toronto, IBA, and Sirtex, and travel support from ViewRay; he participates on an advisory board for ViewRay, and serves on the Board of Directors of the Proton Collaborative Group. KS received funding for the current project through Imaging and Radiation Oncology Core (IROC) grant. EO received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, BioNTech, Ipsen, Merck, Novartis, AstraZeneca, BioSapien, Astellas, Thetis, Autem, Neogene, BMS, Tempus, Fibrogen, Merus, Agios (spouse), Genentech-Roche (spouse), Eisai (spouse) and research finding to her institution from Genentech/Roche, BioNTech, AstraZeneca, Arcus, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Hoosier Cancer Research Network, Kronos Bio, and Mirati Therapeutics Inc; Honorarium/speaker role from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd (to myself), research funds from Celgene/BMS, Roche/Genentech, Janssen, Novartis (to institution). JM is on the advisory board and has received consulting fees from Merck Pharmaceutical. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose. JH received grant funding from the Canopy Cancer Collective (institution), royalties from Springer for a textbook (self), consulting fees from Histosonics and Boston Scientific (self), and has stock in Histosonics.
Figures

References
-
- Ghaneh P, Palmer D, Cicconi S, et al. Immediate surgery compared with short-course neoadjuvant gemcitabine plus capecitabine, FOLFIRINOX, or chemoradiotherapy in patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (ESPAC5): a four-arm, multicentre, randomised, phase 2 trial. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00348-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jang JY, Han Y, Lee H, et al. Oncological Benefits of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation With Gemcitabine Versus Upfront Surgery in Patients With Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: A Prospective, Randomized, Open-label, Multicenter Phase 2/3 Trial. Ann Surg. Aug 2018;268(2):215–222. doi: 10.1097/sla.0000000000002705 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abrams RA, Winter KA, Regine WF, et al. Failure to Adhere to Protocol Specified Radiation Therapy Guidelines Was Associated With Decreased Survival in RTOG 9704—A Phase III Trial of Adjuvant Chemotherapy and Chemoradiotherapy for Patients With Resected Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics. 2012/02/01/ 2012;82(2):809–816. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.039 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

