Involvement of Fgf2-mediated tau protein phosphorylation in cognitive deficits induced by sevoflurane in aged rats
- PMID: 38493090
- PMCID: PMC10943822
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-00784-0
Involvement of Fgf2-mediated tau protein phosphorylation in cognitive deficits induced by sevoflurane in aged rats
Abstract
Objective: Anesthetics have been linked to cognitive alterations, particularly in the elderly. The current research delineates how Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (Fgf2) modulates tau protein phosphorylation, contributing to cognitive impairments in aged rats upon sevoflurane administration.
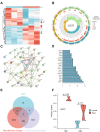
Methods: Rats aged 3, 12, and 18 months were subjected to a 2.5% sevoflurane exposure to form a neurotoxicity model. Cognitive performance was gauged, and the GEO database was employed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the 18-month-old cohort post sevoflurane exposure. Bioinformatics tools, inclusive of STRING and GeneCards, facilitated detailed analysis. Experimental validations, both in vivo and in vitro, examined Fgf2's effect on tau phosphorylation.
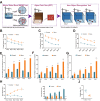
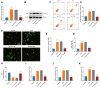
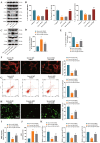
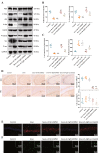
Results: Sevoflurane notably altered cognitive behavior in older rats. Out of 128 DEGs discerned, Fgf2 stood out as instrumental in regulating tau protein phosphorylation. Sevoflurane exposure spiked Fgf2 expression in cortical neurons, intensifying tau phosphorylation via the PI3K/AKT/Gsk3b trajectory. Diminishing Fgf2 expression correspondingly curtailed tau phosphorylation, neurofibrillary tangles, and enhanced cognitive capacities in aged rats.
Conclusion: Sevoflurane elicits a surge in Fgf2 expression in aging rats, directing tau protein phosphorylation through the PI3K/AKT/Gsk3b route, instigating cognitive aberrations.
Keywords: Aged rats; Cognitive impairment; Fgf2; Gsk3b; Sevoflurane; Tau protein phosphorylation; Transcriptomic sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

