Single-cell transcriptomic sequencing data reveal aberrant DNA methylation in SMAD3 promoter region in tumor-associated fibroblasts affecting molecular mechanism of radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38493128
- PMCID: PMC10944599
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05057-2
Single-cell transcriptomic sequencing data reveal aberrant DNA methylation in SMAD3 promoter region in tumor-associated fibroblasts affecting molecular mechanism of radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Objective: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) often exhibits resistance to radiotherapy, posing significant treatment challenges. This study investigates the role of SMAD3 in NSCLC, focusing on its potential in influencing radiosensitivity via the ITGA6/PI3K/Akt pathway.
Methods: The study utilized gene expression data from the GEO database to identify differentially expressed genes related to radiotherapy resistance in NSCLC. Using the GSE37745 dataset, prognostic genes were identified through Cox regression and survival analysis. Functional roles of target genes were explored using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and co-expression analyses. Gene promoter methylation levels were assessed using databases like UALCAN, DNMIVD, and UCSC Xena, while the TISCH database provided insights into the correlation between target genes and CAFs. Experiments included RT-qPCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry on NSCLC patient samples, in vitro studies on isolated CAFs cells, and in vivo nude mouse tumor models.
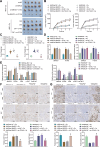
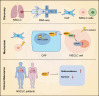
Results: Fifteen key genes associated with radiotherapy resistance in NSCLC cells were identified. SMAD3 was recognized as an independent prognostic factor for NSCLC, linked to poor patient outcomes. High expression of SMAD3 was correlated with low DNA methylation in its promoter region and was enriched in CAFs. In vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed that SMAD3 promotes radiotherapy resistance by activating the ITGA6/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: High expression of SMAD3 in NSCLC tissues, cells, and CAFs is closely associated with poor prognosis and increased radiotherapy resistance. SMAD3 is likely to enhance radiotherapy resistance in NSCLC cells by activating the ITGA6/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: ITGA6; Non-small cell lung cancer; Radiosensitivity; Radiotherapy resistance; SMAD3; Single-cell sequencing; Tumor-associated fibroblasts.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-181a reduces radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer via inhibiting PTEN.Panminerva Med. 2022 Sep;64(3):374-383. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03976-2. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Panminerva Med. 2022. PMID: 32506887
-
SIRT6 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to enhance radiosensitivity of non-Small cell lung cancer and inhibit tumor progression.IUBMB Life. 2021 Sep;73(9):1092-1102. doi: 10.1002/iub.2511. Epub 2021 Jun 4. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 34033225
-
CKS1B regulates the radiosensitivity of lung cancer via activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2025 Aug;132:111828. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111828. Epub 2025 Apr 20. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40262716
-
The PI3-K/AKT-pathway and radiation resistance mechanisms in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Jun;4(6):761-7. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a1084f. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19404218 Review.
-
Novel PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors plus radiotherapy: Strategy for non-small cell lung cancer with mutant RAS gene.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 15;255:117816. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117816. Epub 2020 May 23. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32454155 Review.
Cited by
-
TGM2-Mediated Autophagy Contributes to the Radio-Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Stem-like Cells.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 30;12(10):2231. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102231. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457544 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SLC22A17 DNA methylation hotspot as a potential biomarker in cutaneous melanoma.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 2;22(1):887. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05622-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39358721 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a novel radioresistance-related signature for prediction of prognosis, immune microenvironment and anti-tumour drug sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2447930. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2447930. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39797413 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1 increases the sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma to carbon ion irradiation via HO-1-mediated ferroptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jul;480(7):4265-4281. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05240-z. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40087208
-
Identification of ALDH7A1 as a DNA-methylation-driven gene in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2442529. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2442529. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39711312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li C, Fan K, Qu Y, et al. Deregulation of UCA1 expression may be involved in the development of chemoresistance to cisplatin in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer via regulating the signaling pathway of microRNA-495/NRF2. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3721–3730. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29266. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2009904-01/Key Research and Development Special Sub-Project of National Ministry of Science and Technology
- 81830059/Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22120190219/Special Fund Project of Tongji University Basic Scientific Research Funds of Central Universities
- SHDC2020CR1038B/Major Project of the Clinical Three-Year Action Plan of Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center
- GWV 10.1 XK09/Key Disciplines Construction Plan of Public Health System of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

