Maslinic acid alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 38495003
- PMCID: PMC11187486
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2024027
Maslinic acid alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
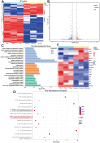
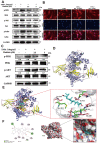
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is the cause of low back pain (LBP), and recent research has suggested that inflammatory cytokines play a significant role in this process. Maslinic acid (MA), a natural compound found in olive plants ( Olea europaea), has anti-inflammatory properties, but its potential for treating IDD is unclear. The current study aims to investigate the effects of MA on TNFα-induced IDD in vitro and in other in vivo models. Our findings suggest that MA ameliorates the imbalance of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and mitigates senescence by upregulating aggrecan and collagen II levels as well as downregulating MMP and ADAMTS levels in nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs). It can also impede the progression of IDD in rats. We further find that MA significantly affects the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways in TNFα-induced NPCs determined by RNA-seq and experimental verification, while the AKT agonist Sc-79 eliminates these signaling cascades. Furthermore, molecular docking simulation shows that MA directly binds to PI3K. Dysfunction of the PI3K/AKT pathway and ECM metabolism has also been confirmed in clinical specimens of degenerated nucleus pulposus. This study demonstrates that MA may hold promise as a therapeutic agent for alleviating ECM metabolism disorders and senescence to treat IDD.
Keywords: NF-κB; PI3K; intervertebral disc degeneration; maslinic acid; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Wang F, Cai F, Shi R, Wang XH, Wu XT. Aging and age related stresses: a senescence mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. . 2016;24:398–408. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.09.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Qiu X, Liang T, Wu Z, Zhu Y, Gao W, Gao B, Qiu J, et al. Melatonin reverses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced metabolic disturbance of human nucleus pulposus cells via MTNR1B/Gαi2/YAP signaling. Int J Biol Sci. . 2022;18:2202–2219. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.65973. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

