Acupuncture modulates the gut microbiota in Alzheimer's disease: current evidence, challenges, and future opportunities
- PMID: 38495110
- PMCID: PMC10940355
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1334735
Acupuncture modulates the gut microbiota in Alzheimer's disease: current evidence, challenges, and future opportunities
Abstract
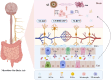
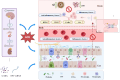
Alzheimer's disease, one of the most severe and common neurodegenerative diseases, has no effective cure. Therefore it is crucial to explore novel and effective therapeutic targets. The gut microbiota - brain axis has been found to play a role in Alzheimer's disease by regulating the neuro-immune and endocrine systems. At the same time, acupuncture can modulate the gut microbiota and may impact the course of Alzheimer's disease. In this Review, we discuss recent studies on the role of acupuncture on the gut microbiota as well current challenges and future opportunities of acupuncture as potential treatment for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; acupuncture; gut microbiota; inflammation; probiotics.
Copyright © 2024 Yan, Li, Qian, Liu, Cong, Dou, Wang, Wang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging role of gut microbiota in modulation of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration with emphasis on Alzheimer's disease.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Mar 2;106:110112. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110112. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32949638 Review.
-
Efficacy of acupuncture in patients with mild Alzheimer's disease and its impact on gut microbiota: Study protocol for a randomized sham-controlled trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 23;10:1014113. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1014113. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36910501 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Modulation of the Gut Microbiota as a Therapeutic Approach for Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022;21(1):14-25. doi: 10.2174/1871527320666210806165751. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34365962 Review.
-
Do the Bugs in Your Gut Eat Your Memories? Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer's Disease.Brain Sci. 2020 Nov 3;10(11):814. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10110814. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33153085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manual acupuncture benignly regulates blood-brain barrier disruption and reduces lipopolysaccharide loading and systemic inflammation, possibly by adjusting the gut microbiota.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 13;14:1018371. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1018371. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36313024 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Study on the mechanism of acupuncture to improve mild cognitive impairment in hypertension by regulating intestinal microbiome.Front Neurosci. 2024 Dec 23;18:1495384. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1495384. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39764388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture Treats Sepsis through Immune Modulation and Organ Protection.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Dec;44(6):1185-1192. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2957-0. Epub 2024 Dec 14. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39673001 Review.
References
-
- Abdelhamid M., Zhou C., Ohno K., Kuhara T., Taslima F., Abdullah M., et al. . (2022b). Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve prevents memory impairment through the reduction of both amyloid-β production and microglia activation in app knock-in mouse. J. Alzheimers Dis. 85, 1555–1571. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215025, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akbari E., Asemi Z., Daneshvar K. R., Bahmani F., Kouchaki E., Tamtaji O. R., et al. . (2016). Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 8:256. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00256, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexandrov P., Zhai Y., Li W., Lukiw W. (2019). Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated, nf-kb-, mirna-146a- and mirna-155-mediated molecular-genetic communication between the human gastrointestinal tract microbiome and the brain. Folia Neuropathol. 57, 211–219. doi: 10.5114/fn.2019.88449, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

