Sipyimigwanjung-tang, a traditional herbal medication, alleviates weight gain in a high-fat diet-induced obese mice model
- PMID: 38495187
- PMCID: PMC10943437
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27463
Sipyimigwanjung-tang, a traditional herbal medication, alleviates weight gain in a high-fat diet-induced obese mice model
Abstract
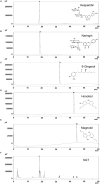
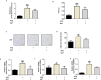
Obesity leads to the development of metabolic syndrome and comorbidities. Overweight and obesity continue to be a relentless global issue. Sipyimigwanjung-tang (SGT), a traditional herbal medication, was first mentioned in Dongui Sasang Shinpyun and has been used to treat edema, meteorism, and jaundice, which are common findings associated with obesity. The main physiological feature of obesity is expanded adipose tissue, which causes several impairments in liver metabolism. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the anti-obesity effects of SGT in the epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) and livers of high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice. SGT significantly blocked HFD-induced weight gain in C57BL/6N mice. In addition, SGT effectively reduced the increased weight and adipocyte size in eWAT of HFD-induced obese C57BL/6 N mice. Moreover, SGT significantly decreased the elevated gene expression of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α, and Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 in the eWAT of HFD-induced obese mice. Furthermore, SGT significantly decreased lipid accumulation in the livers of HFD-induced obese mice and differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Hence, the present study provides substantial evidence that SGT has potential therapeutic effects on obesity.
Keywords: Adipogenesis; High-fat diet; Obesity; Sipyimigwanjung-tang; White adipose tissue.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Polyzos S.A., Kountouras J., Mantzoros C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism. 2019;92:82–97. - PubMed
-
- Singh A.K., Singh R. Pharmacotherapy in obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of anti-obesity drugs. Expet Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020;13(1):53–64. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava G., Apovian C. Future pharmacotherapy for obesity: new anti-obesity drugs on the horizon. Curr Obes Rep. 2018;7(2):147–161. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

