Dominant NARS1 mutations causing axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease expand NARS1-associated diseases
- PMID: 38495304
- PMCID: PMC10943570
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae070
Dominant NARS1 mutations causing axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease expand NARS1-associated diseases
Abstract
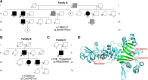
Pathogenic variants in six aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) genes are implicated in neurological disorders, most notably inherited peripheral neuropathies. ARSs are enzymes that charge tRNA molecules with cognate amino acids. Pathogenic variants in asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase (NARS1) cause a neurological phenotype combining developmental delay, ataxia and demyelinating peripheral neuropathy. NARS1 has not yet been linked to axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Exome sequencing of patients with inherited peripheral neuropathies revealed three previously unreported heterozygous NARS1 variants in three families. Clinical and electrophysiological details were assessed. We further characterized all three variants in a yeast complementation model and used a knock-in mouse model to study variant p.Ser461Phe. All three variants (p.Met236del, p.Cys342Tyr and p.Ser461Phe) co-segregate with the sensorimotor axonal neuropathy phenotype. Yeast complementation assays show that none of the three NARS1 variants support wild-type yeast growth when tested in isolation (i.e. in the absence of a wild-type copy of NARS1), consistent with a loss-of-function effect. Similarly, the homozygous knock-in mouse model (p.Ser461Phe/Ser472Phe in mouse) also demonstrated loss-of-function characteristics. We present three previously unreported NARS1 variants segregating with a sensorimotor neuropathy phenotype in three families. Functional studies in yeast and mouse support variant pathogenicity. Thus, NARS1 is the seventh ARS implicated in dominant axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, further stressing that all dimeric ARSs should be evaluated for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
Keywords: Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease; NARS1; aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase; axonal sensorimotor neuropathy.
© Crown copyright 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Schimmel PR, Soll D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: General features and recognition of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:601–648. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
