The Role of Probiotics in the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori and Overall Impact on Management of Peptic Ulcer: A Study Involving Patients Undergoing Triple Therapy in Bangladesh
- PMID: 38495972
- PMCID: PMC10944298
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.56283
The Role of Probiotics in the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori and Overall Impact on Management of Peptic Ulcer: A Study Involving Patients Undergoing Triple Therapy in Bangladesh
Abstract
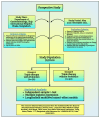
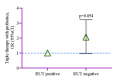
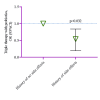
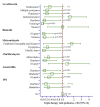
Background Helicobacter pylori infection has been identified to cause constantly recurring inflammation, leading to gastrointestinal tract disorders, including carcinoma. The standard triple therapy (STT), used to eradicate H. pylori, includes two antimicrobials and a proton pump inhibitor for two weeks. Other drug regimens have also been developed since H. pylori exhibits antimicrobial resistance. These regimens, including probiotics, have been shown to lower adverse drug reactions (ADR), improve drug adherence, exert bacteriostatic effect, and reduce inflammation. Objective This study intended to explore probiotic intervention for improving eradication rates and mitigating adverse effects while administrating STT. Methods This prospective study was conducted from May to December, 2021, in the Department of Gastroenterology of Ship International Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, to observe the effects of probiotics inclusion along with STT on H. pylori eradication. A total of 100 patients aged ≥18 years who tested positive for H. pylori were included. The experimental group (n=50) was given STT and probiotics, and the control group (n=50) was given only STT without probiotics for 14 days. Necessary follow-up was done six weeks after treatment. An independent sample t-test, chi-square test, and multiple regression analysis were used for statistical analysis. Result The odds of getting rapid urease test (RUT) negative results from positive were 2.06 times higher (95%CI= 0.95, 3.22, p=0.054) in the experimental group. ADRs were crucially towering in the control group (p=0.045) compared to the probiotics group. The probiotics group had a lower risk of having adverse effects by 0.54 times (95%CI=0.19, 0.84, p=0.032) than the control group. Conclusion Using probiotics and STT together to eradicate H. pylori may lower ADR and improve treatment adherence. It may also help terminate H. pylori infection more effectively. More research is required as H. pylori is very contagious and can ultimately cause life-threatening gastric cancer.
Keywords: bangladesh; h. pylori treatment; helicobacter pylori; peptic ulcer disease; probiotic bacterium; probiotic microflora; pud; triple therapy.
Copyright © 2024, Zaman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Probiotics improve the efficacy of standard triple therapy in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a meta-analysis.Infect Drug Resist. 2016 Dec 7;9:275-289. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S117886. eCollection 2016. Infect Drug Resist. 2016. PMID: 27994474 Free PMC article.
-
Can probiotics improve efficiency and safety profile of triple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy? A prospective randomized study.Vojnosanit Pregl. 2016 Nov;73(11):1044-9. doi: 10.2298/VSP150415127G. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2016. PMID: 29328644 Clinical Trial.
-
Adjuvant probiotics improve the eradication effect of triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Nov 21;18(43):6302-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6302. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23180952 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Probiotic Supplementation Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 10;11(10):e0163743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163743. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27723762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are probiotics useful in Helicobacter pylori eradication?World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 7;21(37):10644-53. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10644. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26457024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Inhibitory Effects of Probiotic Bacteria and Propolis Extracts on the Growth and Histopathological Changes in Gastric Tissues of Helicobacter pylori Challenged Wistar Rats.Iran J Pharm Res. 2024 Dec 25;23(1):e148158. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-148158. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 40066122 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Pyloshot in combination with standard four-drug antimicrobial treatment for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized clinical trial.JGH Open. 2024 Dec 8;8(12):e70046. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.70046. eCollection 2024 Dec. JGH Open. 2024. PMID: 39655241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The prevalence and incidence of Helicobacter pylori-associated peptic ulcer disease and upper gastrointestinal bleeding throughout the world. Wang AY, Peura DA. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2011;21:613–635. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
