Evaluation of Osteoconductive and Antimicrobial Properties of Novel Graphene on Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 38496143
- PMCID: PMC10941632
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.54172
Evaluation of Osteoconductive and Antimicrobial Properties of Novel Graphene on Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
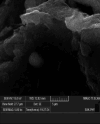
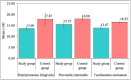
Introduction Graphene oxide (GO) has emerged as a promising material in dentistry, leveraging its exceptional properties. This study evaluates the physicochemical attributes of GO and elucidates its derived biological properties. These encompass biocompatibility, antibacterial efficacy, as well as its influence on osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation processes. Understanding the intricate interplay between the physicochemical and biological aspects of GO provides valuable insights into its potential applications in various dental contexts. Materials and methods The study group (so; titanium discs surface coated with GO) and the control group (co; plain/uncoated machined titanium discs) were divided based on cell attachment and cell proliferation assays (n=60). These groups were further divided into subgroups (n=30) based on the tested time intervals, specifically 24 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours. The study and controlgroups were further subdivided into three subgroups (n=10) based on the microorganisms tested i.e Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia and Fusobacteria nucleatum. Results The results of this in vitro study suggest that GO-coated titanium dental implants have both increased osteogenic potential and antimicrobial efficacy. Graphene has good potential as a promising alternative to traditional surface treatments, and a graphene-coated implant can be used for enhanced osseointegration. Conclusion The osteogenic potential and the cell attachment were higher on titanium surfaces coated with GO nanoparticles when compared to plain titanium discs at 24, 48 and 72 hours respectively.
Keywords: bacterial strains; graphene oxide; implant coating; implant osseointegration; surface modification.
Copyright © 2024, Rayannavar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Clinical manual of implant dentistry. Davis D. Br Dent J. 2004;196:118.
-
- Implant dentistry and the concept of osseointegration: a historical perspective. Sullivan RM. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2001;29:737–745. - PubMed
-
- Peri-implant mucositis. Heitz-Mayfield LJ, Salvi GE. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45 Suppl 20:0–45. - PubMed
-
- Reversibility of experimental peri-implant mucositis compared with experimental gingivitis in humans. Salvi GE, Aglietta M, Eick S, Sculean A, Lang NP, Ramseier CA. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23:182–190. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
