This is a preprint.
HPV18 E7 inhibits LATS1 kinase and activates YAP1 by degrading PTPN14
- PMID: 38496413
- PMCID: PMC10942435
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.07.583953
HPV18 E7 inhibits LATS1 kinase and activates YAP1 by degrading PTPN14
Update in
-
HPV18 E7 inhibits LATS1 kinase and activates YAP1 by degrading PTPN14.mBio. 2024 Oct 16;15(10):e0181124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01811-24. Epub 2024 Sep 9. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39248565 Free PMC article.
Abstract
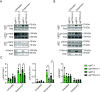
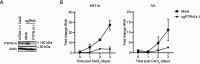
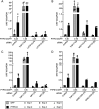
High-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) oncoproteins inactivate cellular tumor suppressors to reprogram host cell signaling pathways. HPV E7 proteins bind and degrade the tumor suppressor PTPN14, thereby promoting the nuclear localization of the YAP1 oncoprotein and inhibiting keratinocyte differentiation. YAP1 is a transcriptional coactivator that drives epithelial cell stemness and self-renewal. YAP1 activity is inhibited by the highly conserved Hippo pathway, which is frequently inactivated in human cancers. MST1/2 and LATS1/2 kinases form the core of the Hippo kinase cascade. Active LATS1 kinase is phosphorylated on threonine 1079 and inhibits YAP1 by phosphorylating it on amino acids including serine 127. Here, we tested the effect of high-risk (carcinogenic) HPV18 E7 on Hippo pathway activity. We found that either PTPN14 knockout or PTPN14 degradation by HPV18 E7 decreased phosphorylation of LATS1 T1079 and YAP1 S127 in human keratinocytes and inhibited keratinocyte differentiation. Conversely, PTPN14-dependent differentiation required LATS kinases and certain PPxY motifs in PTPN14. Neither MST1/2 kinases nor the putative PTPN14 phosphatase active site were required for PTPN14 to promote differentiation. Taken together, these data support that PTPN14 inactivation or degradation of PTPN14 by HPV18 E7 reduce LATS1 activity, promoting active YAP1 and inhibiting keratinocyte differentiation.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Hippo; Human papillomavirus; Microbiology; PTPN14; YAP1; differentiation; keratinocyte; tumor suppressor.
Figures





References
-
- McBride A. A., Human papillomaviruses: diversity, infection and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 20, 95–108 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Moody C. A., Laimins L. A., Human papillomavirus oncoproteins: pathways to transformation. Nat Rev Cancer 10, 550–560 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Munger K., Harlow E., The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science 243, 934–937 (1989). - PubMed
-
- DeGregori J., Johnson D. G., Distinct and Overlapping Roles for E2F Family Members in Transcription, Proliferation and Apoptosis. Curr Mol Med 6, 739–748 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
