This is a preprint.
Uncalled4 improves nanopore DNA and RNA modification detection via fast and accurate signal alignment
- PMID: 38496646
- PMCID: PMC10942365
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583511
Uncalled4 improves nanopore DNA and RNA modification detection via fast and accurate signal alignment
Update in
-
Uncalled4 improves nanopore DNA and RNA modification detection via fast and accurate signal alignment.Nat Methods. 2025 Apr;22(4):681-691. doi: 10.1038/s41592-025-02631-4. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 40155722 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Nanopore signal analysis enables detection of nucleotide modifications from native DNA and RNA sequencing, providing both accurate genetic/transcriptomic and epigenetic information without additional library preparation. Presently, only a limited set of modifications can be directly basecalled (e.g. 5-methylcytosine), while most others require exploratory methods that often begin with alignment of nanopore signal to a nucleotide reference. We present Uncalled4, a toolkit for nanopore signal alignment, analysis, and visualization. Uncalled4 features an efficient banded signal alignment algorithm, BAM signal alignment file format, statistics for comparing signal alignment methods, and a reproducible de novo training method for k-mer-based pore models, revealing potential errors in ONT's state-of-the-art DNA model. We apply Uncalled4 to RNA 6-methyladenine (m6A) detection in seven human cell lines, identifying 26% more modifications than Nanopolish using m6Anet, including in several genes where m6A has known implications in cancer. Uncalled4 is available open-source at github.com/skovaka/uncalled4.
Figures
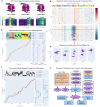
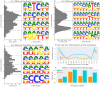
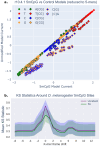
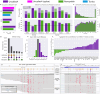
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
