HER3 overexpression: a predictive marker for poor prognosis in advanced ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treated with ALK inhibitors
- PMID: 38496685
- PMCID: PMC10938092
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-804
HER3 overexpression: a predictive marker for poor prognosis in advanced ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treated with ALK inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) improve patient survival; however, some patients develop ALK-TKI resistance with unidentified mechanisms. We investigated ErbB family and c-MET expression in patients with ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to understand their roles in the ALK-TKI response.
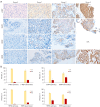
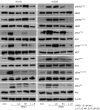
Methods: We studied 72 patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC with EML4-ALK fusion variant subtyping and immunostaining for c-MET, EGFR, HER2, and HER3 on tissue specimens both pre- (primary) and post-treatment (secondary) with ALK-TKI. We investigated the association of their expression with survival outcomes and assessed the effectiveness of combining ALK and EGFR inhibitors in ALK-positive NSCLC cell lines stimulated with the HER3-specific ligand HRG1.
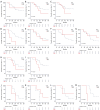
Results: High expression of c-MET, EGFR, HER2, and HER3 was observed in 4.9%, 18.0%, 1.6%, and 25.8% of primary tumors, respectively, and 18.5%, 37.0%, 10.7%, and 35.7% of secondary tumors, respectively. HER3 overexpression in primary tumors showed inferior survival (P=0.132). In the subgroup with EML4-ALK variant 1/2 (V1/V2), HER3 overexpression was significantly associated with inferior survival in both primary and secondary tumors (P=0.022 and P=0.004, respectively). Combination treatment with lorlatinib and erlotinib significantly reduced HRG1-induced activation of RTK signaling in ALK-positive NSCLC cells.
Conclusions: HER3 overexpression has potential as a prognostic marker in ALK-positive NSCLCs, including ALK-TKI naïve and treated cases, especially those with EML4-ALK V1/V2. Assessing HER3 expression may be crucial for treatment planning and outcome prediction in these patients.
Keywords: EGFR; EML4-ALK; HER3; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); c-MET.
2024 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-804/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
