Osimertinib in uncommon EGFR exon 21 L861R and EGFR exon 18 deletion-insertion mutant non-small cell lung cancer-case report
- PMID: 38496692
- PMCID: PMC10938107
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-788
Osimertinib in uncommon EGFR exon 21 L861R and EGFR exon 18 deletion-insertion mutant non-small cell lung cancer-case report
Abstract
Background: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have changed the treatment landscape for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) found to have oncogene-driven activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. Whilst there have been a handful of case reports of sensitivity to first-generation TKIs in EGFR L861R mutations, the efficacy of the third-generation TKI osimertinib in NSCLC patients with EGFR L861R and EGFR exon 18 deletion-insertion mutations is limited.
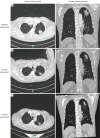
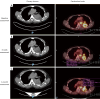
Case description: We report two patients from our institution with uncommon EGFR mutations treated with first-line osimertinib. Our first patient, a 72-year-old male with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma was identified to harbour a rare EGFR L861R mutation and was commenced on osimertinib. After a follow-up period of 18 months, the patient is continuing to experience treatment benefit with imaging showing a good partial response. The second patient, a 60-year-old male also with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma and an EGFR exon 18 deletion-insertion mutation achieved a partial response for 6.6 months. Upon progression, he was commenced on carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy however died from subsequent pneumonia. He had an overall survival (OS) from time of diagnosis of 7.6 months.
Conclusions: We demonstrate clinical efficacy of first-line osimertinib in the treatment of advanced NSCLC harbouring uncommon EGFR L861R and EGFR exon 18 deletion-insertion mutations. These results may be suggestive of the wider applicability of osimertinib in the treatment of uncommon EGFR mutant NSCLC.
Keywords: Uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR mutations (uncommon EGFR mutations); case report; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); osimertinib.
2024 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-788/coif). S.A. reports speaker fees from Merck-Sharpe & Dohme, Astra Zeneca, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb; travel support from Astra Zeneca, Roche, Merck-Sharpe & Dohme; non-financial aid from Astra Zeneca, Pfizer; and Advisory Boards of Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Afatinib overcoming resistance to icotinib and osimertinib in NSCLC with leptomeningeal metastasis in patients with acquired EGFR L858R/T790M or L858R/S768I mutations: Two case reports.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 8;9(10):e20690. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20690. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37860534 Free PMC article.
-
A non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient harboring a rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) L858R/V843I mutation complex benefited from osimertinib: a case report.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Mar;11(3):1121-1125. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2653. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 35365042
-
A non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient with leptomeningeal metastasis harboring rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations G719S and L861Q benefited from doubling dosage of osimertinib: a case report.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 May;10(5):5897-5901. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-2556. Epub 2021 May 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33977730
-
Overall Treatment Strategy for Patients With Metastatic NSCLC With Activating EGFR Mutations.Clin Lung Cancer. 2022 Jan;23(1):e69-e82. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2021.10.009. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Clin Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34865963 Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
