Biomarkers for predicting atrial fibrillation: An explorative sub-analysis of the randomised SCREEN-AF trial
- PMID: 38497412
- PMCID: PMC10949835
- DOI: 10.1080/13814788.2024.2327367
Biomarkers for predicting atrial fibrillation: An explorative sub-analysis of the randomised SCREEN-AF trial
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common treatable risk factor for stroke. Screening for paroxysmal AF in general practice is difficult, but biomarkers might help improve screening strategies.
Objectives: We investigated six blood biomarkers for predicting paroxysmal AF in general practice.
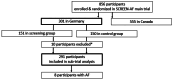
Methods: This was a pre-specified sub-study of the SCREEN-AF RCT done in Germany. Between 12/2017-03/2019, we enrolled ambulatory individuals aged 75 years or older with a history of hypertension but without known AF. Participants in the intervention group received active AF screening with a wearable patch, continuous ECG monitoring for 2x2 weeks and usual care in the control group. The primary endpoint was ECG-confirmed AF within six months after randomisation. High-sensitive Troponin I (hsTnI), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro BNP), N-terminal pro atrial natriuretic peptide (NT-ANP), mid-regional pro atrial natriuretic peptide (MR-pro ANP) and C-reactive protein (CRP) plasma levels were investigated at randomisation for predicting AF within six months after randomisation.
Results: Blood samples were available for 291 of 301 (96.7%) participants, including 8 with AF (3%). Five biomarkers showed higher median results in AF-patients: BNP 78 vs. 41 ng/L (p = 0.012), NT-pro BNP 273 vs. 186 ng/L (p = 0.029), NT-proANP 4.4 vs. 3.5 nmol/L (p = 0.027), MR-pro ANP 164 vs. 125 pmol/L (p = 0.016) and hsTnI 7.4 vs. 3.9 ng/L (p = 0.012). CRP levels were not different between groups (2.8 vs 1.9 mg/L, p = 0.1706).
Conclusion: Natriuretic peptide levels and hsTnI are higher in patients with AF than without and may help select patients for AF screening, but larger trials are needed.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02392754; natriuretic peptides; prediction; primary care; screening; www.DZHK.de: SCREEN-AF DZHK15.
Plain language summary
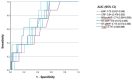
BNP, NT-pro BNP, NT-ANP and MR-pro ANP and hsTnI levels are higher in patients with AF than without AFWith a sensitivity at 100%, BNP had the highest specificity of 60% (BNP level 50.1ng/L), followed by NT-pro BNP with a specificity of 53% (179ng/l).
Conflict of interest statement
JH has research grants and speaking fees from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, BMS/Pfizer, Servier and consulting fees from Bayer. DG reported receiving an operating grant from the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network (C-SPIN) during the conduct of the main SCREEN-AF trial (C-SPIN is a peer-reviewed national network grant funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [CIHR]). He was supported by a Mid-Career Investigator Award from the Heart and Stroke Foundation (Canada) and the Department of Medicine and Bastable-Potts Chair at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto. He serves as a Canadian national co-leader for the ARCADIA trial. He received an honorarium for participation in ad hoc advisory board for HLS Therapeutics Inc. He has had no personal financial relationships with cardiac monitoring device manufacturers or pharmaceutical companies related to AF in the past 6+ years. RW reports receiving grants from Deutsches Zentrum für Herz-/Kreislaufforschung for the conduct of the study, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, European Union, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic; personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Daiichi-Sankyo, BMS, Medtronic, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, sciarc and Servier outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of NT-proANP and NT-proBNP in patients with atrial fibrillation: Association with atrial fibrillation progression phenotypes.Heart Rhythm. 2018 Aug;15(8):1132-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.03.021. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Heart Rhythm. 2018. PMID: 29604419
-
Direct comparison of mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide with N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of patients with atrial fibrillation and dyspnoea.Heart. 2012 Oct;98(20):1518-22. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2012-302260. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Heart. 2012. PMID: 22865868
-
B-type natriuretic peptide over N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide to predict incident atrial fibrillation after cryptogenic stroke.Eur J Neurol. 2021 Feb;28(2):540-547. doi: 10.1111/ene.14579. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33043545
-
Atrial Fibrillation, thromboembolic risk, and the potential role of the natriuretic peptides, a focus on BNP and NT-proBNP - A narrative review.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022 Oct 10;43:101132. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101132. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022. PMID: 36246770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative B-Type Natriuretic Peptides to Predict Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation in Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Heart Lung Circ. 2024 Jan;33(1):23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2023.10.015. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Heart Lung Circ. 2024. PMID: 38143193
Cited by
-
Evidence Gaps and Lessons in the Early Detection of Atrial Fibrillation: A Prospective Study in a Primary Care Setting (PREFATE Study).Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):119. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010119. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857703 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NT-proBNP in screening for atrial fibrillation in hypertensive disease.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Nov 8;55:101549. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101549. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39911617 Free PMC article.
-
Low Levels of Adropin Predicted New Incidents of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.Biomolecules. 2025 Aug 15;15(8):1171. doi: 10.3390/biom15081171. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40867615 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of NT-proBNP reduction on recurrence after cryoballoon pulmonary vein isolation and left atrial roof ablation in persistent atrial fibrillation.Heart Vessels. 2025 Jun 6. doi: 10.1007/s00380-025-02559-x. Online ahead of print. Heart Vessels. 2025. PMID: 40478446
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous