Quantitative analysis of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria antibodies in sera and breast milk from Tdap vaccinated women using a qualified multiplex assay
- PMID: 38497618
- PMCID: PMC11036809
- DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00527-23
Quantitative analysis of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria antibodies in sera and breast milk from Tdap vaccinated women using a qualified multiplex assay
Abstract
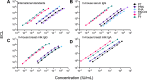
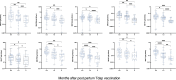
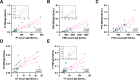
Pertussis (whooping cough) is a reemergent, highly contagious respiratory infection of public health concern. Infants prior to initiation of their primary vaccination series are the most vulnerable to severe infection, and even death. Vaccination during pregnancy is an efficacious means of reducing infection in infants. This approach relies on boosting maternal immunity and passive transfer of antibodies to the infant via placenta and breast milk. Similarly, maternal vaccination post-partum can enhance maternal-infant immunity. To support the analysis of pertussis immunity in the context of maternal-infant immunization, we developed a high throughput multiplex assay for simultaneous quantification of serum IgG antibodies against pertussis vaccine antigens: pertussis toxin (PT), filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), pertactin (PRN), and fimbriae (FIM2/3), and against tetanus (TT) and diphtheria toxoids (DT), using the Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) platform. The assay was qualified, and specificity, sensitivity, accuracy, precision, linearity, and robustness were demonstrated. The assay was subsequently adapted for quantification of IgG and IgA in breast milk. Applied to a serological survey of pregnant women living in the United States and sub-Saharan Africa, this method revealed differences in magnitude and breadth of antibody profile, consistent with history of vaccination. A longitudinal analysis of Tdap responses in women vaccinated post-partum demonstrated a rapid increase in serum IgG that remained elevated for up to 24 months. Likewise, high levels of vaccine-specific IgA and IgG antibodies were present in breast milk, although they exhibited faster decay. This multiplex MSD assay is a reliable and practical tool for quantification of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria antibodies in serum and breast milk in serosurveys or vaccine studies.
Importance: Pertussis (whooping cough) has reemerged in recent years. Vaccination during pregnancy is an effective approach to prevent illness during the first months of life. We developed a multiplex assay for quantification of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria serum antibodies using the Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) platform; the method was qualified, and specificity, precision, accuracy, linearity, and limits of quantification were defined. It was also adapted for quantification of antibodies in breast milk. We successfully determined serostatus in women from different regions and with different vaccination histories, as well as responses to Tdap in blood and breast milk post-partum. This is the first description of a multiplex assay for the quantification of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria antibodies in breast milk.
Keywords: Tdap; infant immunity; infant vaccines; maternal vaccines; multiplex; pertussis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Halperin BA, Morris A, Mackinnon-Cameron D, Mutch J, Langley JM, McNeil SA, Macdougall D, Halperin SA. 2011. Kinetics of the antibody response to tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine in women of childbearing age and postpartum women. Clin Infect Dis 53:885–892. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir538 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abu Raya B, Srugo I, Kessel A, Peterman M, Bader D, Peri R, Ashtamker N, Gonen R, Bamberger E. 2014. The induction of breast milk pertussis specific antibodies following gestational tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccination. Vaccine 32:5632–5637. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.08.006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
