Safe Farming: Ultrafine Bubble Water Reduces Insect Infestation and Improves Melon Yield and Quality
- PMID: 38498517
- PMCID: PMC10891724
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13040537
Safe Farming: Ultrafine Bubble Water Reduces Insect Infestation and Improves Melon Yield and Quality
Abstract
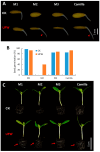
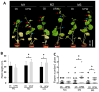
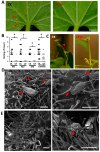
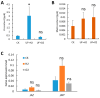
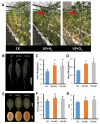
Melon pest management relies on the excessive application of pesticides. Reducing pesticide spraying has become a global issue for environmental sustainability and human health. Therefore, developing a new cropping system that is sustainable and eco-friendly is important. This study found that melon seedlings irrigated with ultrafine water containing H2 and O2 (UFW) produced more root hairs, increased shoot height, and produced more flowers than the control irrigated with reverse osmosis (RO) water. Surprisingly, we also discovered that UFW irrigation significantly reduced aphid infestation in melons. Based on cryo-scanning electron microscope (cryo-SEM) observations, UFW treatment enhanced trichome development and prevented aphid infestation. To investigate whether it was H2 or O2 that helped to deter insect infestation, we prepared UF water enrichment of H2 (UF+H2) and O2 (UF+O2) separately and irrigated melons. Cryo-SEM results indicated that both UF+H2 and UF+O2 can increase the density of trichomes in melon leaves and petioles. RT-qPCR showed that UF+H2 significantly increased the gene expression level of the trichome-related gene GLABRA2 (GL2). We planted melons in a plastic greenhouse and irrigated them with ultrafine water enrichment of hydrogen (UF+H2) and oxygen (UF+O2). The SPAD value, photosynthetic parameters, root weight, fruit weight, and fruit sweetness were all better than the control without ultrafine water irrigation. UFW significantly increased trichome development, enhanced insect resistance, and improved fruit traits. This system thus provides useful water management for pest control and sustainable agricultural production.
Keywords: jasmonate; muskmelon; nanobubbles water; pest damage; trichome; yield.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Ning Juan Li, Ching Yen Peng, and Ching Chieh Yang, were employed by the company Season Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd., Tainan, Taiwan. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ushikubo F.Y., Furukawa T., Nakagawa R., Enari M., Makino Y., Kawagoe Y., Shiina T., Oshita S. Evidence of the existence and the stability of nano-bubbles in water. Colloids Surf. A. 2010;361:31–37. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.03.005. - DOI
-
- Li L.N., Zeng Y., Cheng X., Shen W.B. The applications of molecular hydrogen in horticulture. Horticulturae. 2021;7:513. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7110513. - DOI
-
- Takahata J., Takaki K., Satta N., Takahashi K., Fujio T., Sasaki Y. Improvement of growth rate of plants by bubble discharge in water. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014;54:01AG07. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.54.01AG07. - DOI
-
- Lee S.Y., Jeong S., Cho A.R., Shim M.S., Chung Y.K., Kim Y.J. Germination and seedling growth response of sprouts and leafy vegetables after applying oxygen nanobubble water. J. People Plants Environ. 2021;24:607–617. doi: 10.11628/ksppe.2021.24.6.609. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

