Exploring drivers of unsafe disposal of child stool in India using hierarchical regression model
- PMID: 38498574
- PMCID: PMC10947681
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295788
Exploring drivers of unsafe disposal of child stool in India using hierarchical regression model
Abstract
Background: Disposal of children's stools is often neglected in Indian sanitation programs, putting them at higher risk of diseases transmitted through the fecal-oral route. Therefore, the current study aims to identify the socioeconomic and demographic factors associated with the unsafe disposal of child stool in India and to estimate the geographical variation in unsafe disposal.
Methods: The study used 78,074 births under two years from the fifth round of the National Family Health Survey (2019-21). Descriptive statistics, bivariate analysis with the chi-square test, and a four-level hierarchical logistic regression model were applied to accomplish the study objectives.
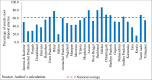
Results: Findings revealed a 61.3% prevalence of unsafe stool disposal nationwide, significantly varying between rural (45%) and urban (67%) areas. Multilevel logistic regression highlighted that mother's education, wealth quintile, and sanitation facility were significant predictors of unsafe disposal of child stools. Random intercept statistics revealed a substantial geographical unit-level variance in unsafe stool practice in India.
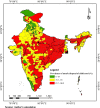
Conclusion: The study emphasizes the widespread unsafe disposal of child stool among Indian mothers with young children below two years, and the study underscores a range of contributing factors, including education, media exposure, prosperity, water availability, and sanitation. It also accentuates the significance of the geographical variance in the unsafe disposal of child stool in India, particularly at the household level, followed by the community level. Hence, the findings underscore the importance of focused interventions, including targeted household-level poverty alleviation programs, initiatives to enhance sanitation and water facilities, and community-level public health awareness programs.
Copyright: © 2024 Rahaman et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ngure FM, Humphrey JH, Mbuya MN, Majo F, Mutasa K, Govha M, et al. Formative research on hygiene behaviors and geophagy among infants and young children and implications of exposure to fecal bacteria. The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene. 2013;89(4):709. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0568 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saha J, Mondal S, Chouhan P, Hussain M, Yang J, Bibi A. Occurrence of Diarrheal Disease among Under-Five Children and Associated Sociodemographic and Household Environmental Factors: An Investigation Based on National Family Health Survey-4 in Rural India. Children. 2022;9(5):658. doi: 10.3390/children9050658 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roy E, Hasan KZ, Haque R, Haque AF, Siddique AK, Sack RB. Patterns and risk factors for helminthiasis in rural children aged under 2 in Bangladesh. South African Journal of Child Health. 2011;5(3):78–84.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources