The comprehensive landscape of prognosis, immunity, and function of the GLI family by pan-cancer and single-cell analysis
- PMID: 38498906
- PMCID: PMC11006459
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205630
The comprehensive landscape of prognosis, immunity, and function of the GLI family by pan-cancer and single-cell analysis
Abstract
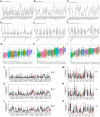
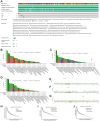
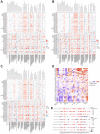
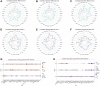
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various cancers. However, the roles of the downstream GLI family (GLI1, GLI2, and GLI3) in tumorigenesis remain elusive. This study aimed to unravel the genetic alterations of GLI1/2/3 in cancer and their association with the immune microenvironment and related signaling pathways. Firstly, we evaluated the expression profiles of GLI1/2/3 in different cancer types, analyzed their prognostic and predictive values, and assessed their correlation with tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Secondly, we explored the relationships between GLI1/2/3 and genetic mutations, epigenetic modifications, and clinically relevant drugs. Finally, we performed enrichment analysis to decipher the underlying mechanisms of GLI1/2/3 in cancer initiation and progression. Our results revealed that the expression levels of GLI1/2/3 were positively correlated in most cancer tissues, suggesting a cooperative role of these factors in tumorigenesis. We also identified tissue-specific expression patterns of GLI1/2/3, which may reflect the distinct functions of these factors in different cell types. Furthermore, GLI1/2/3 expression displayed significant associations with poor prognosis in several cancers, indicating their potential as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Importantly, we found that GLI1/2/3 modulated the immune microenvironment by regulating the recruitment, activation, and polarization of cancer-associated fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and macrophages. Additionally, functional enrichment analyses indicated that GLI1/2/3 are involved in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Together, our findings shed new light on the roles of GLI1/2/3 in tumorigenesis and provide a potential basis for the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting GLI-mediated signaling pathways in cancer.
Keywords: GLI; function; immune; pan-cancer; prognosis; single-cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures










References
-
- Wei SC, Duffy CR, Allison JP. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018; 8:1069–86. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

