Estimate the burden of malnutrition among children with cerebral palsy in Sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- PMID: 38499717
- PMCID: PMC10948888
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55730-1
Estimate the burden of malnutrition among children with cerebral palsy in Sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Abstract
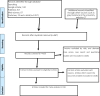
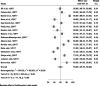
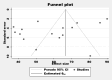
Malnutrition is more prevalent among children with cerebral palsy and a major factor for child morbidity and mortality in children with different co-morbidity, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa: The main aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to estimate the burden of malnutrition among children with cerebral palsy in Sub-Saharan Africa. We searched PubMed, Web of Science, Google Scholar, Research Gate, and institutional repositories for papers that reported the proportion of malnutrition among children with cerebral palsy that were published between December 2010 and September 2023. Data were retrieved using the standardized JBI data extraction checklist through Microsoft Excel, and then exported to STATA 17 for further analysis. DerSimonian and Laird's estimator was used to calculate the pooled effect size in the random-effects model. Statistics such as the Cochran Q test and I2 test were employed to measure heterogeneity. Egger's test and the funnel plot were used to look for publication bias. This systematic review and meta-analysis used 16 studies from Sub-Saharan Africa to estimate the proportion of malnutrition among 2,120 children with cerebral palsy. The pooled proportion of malnutrition among children with cerebral palsy in Sub-Saharan Africa by using random-effects model analysis was found to be 59.7% (95% CI; 49.8-69.6). The proportion of malnutrition was also estimated by sample sizes categorized as ≤ 120 and > 120, and the proportion of malnutrition was found to be 54.0 (95% CI: 44.7-63.3) and 64.5 (95% CI: 50.5-78.5). Moreover, the proportion of malnutrition was estimated by accounting for the difference in the year of publication. In this regard, the study classified before ≤ 2017 and > 2017, and the proportion of malnutrition was found to be 53.7 (95% CI: 38.0-69.3) and 62.5 (95% CI: 49.7-75.3) in Sub-Saharan Africa respectively. Malnutrition among children with cerebral in Sub-Saharan Africa was found to be very high. Hence, enhancing and developing strategic guidelines for malnutrition screening, prevention, and nutritional support are crucial among children with cerebral palsy. Furthermore, systematic review, randomized control trials, and qualitative studies are recommended to understand the burden more among children with cerebral palsy in the continent.
Keywords: Children with cerebral palsy; Malnutrition; Sub-Saharan Africa.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proportion of good oral hygiene and mean value oral hygiene index among children with cerebral palsy in Africa and Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Dec 5;24(1):1480. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05264-9. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39639294 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of early neonatal mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa. A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 25;19(7):e0306297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306297. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39052580 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of gestational age, low birth weight and parity on birth asphyxia among neonates in sub-Saharan Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis: 2021.Ital J Pediatr. 2022 Jul 15;48(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13052-022-01307-5. Ital J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35841063 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and its predictors in abdominal injury across sub-Saharan Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Emerg Med. 2024 Apr 11;24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12873-024-00982-3. BMC Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38605305 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of undernutrition and associated factors among adults taking antiretroviral therapy in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 24;18(3):e0283502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283502. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36961844 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship between nutritional assessment and nutritional risk screening in hospitalized children with cerebral palsy: a single-center prospective study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 28;15(1):27396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12628-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40721852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023 [cited 2023 Dec 7]. What is cerebral palsy? | CDC. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/cp/facts.html
-
- Cerebral Palsy Guidance [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 19]. Cerebral Palsy and Malnutrition. Available from: https://www.cerebralpalsyguidance.com/cerebral-palsy/associated-disorder...
-
- Failure to Thrive [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 19]. Available from: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/failure-t...

