Lac-Phe mediates the effects of metformin on food intake and body weight
- PMID: 38499766
- PMCID: PMC11062621
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-00999-9
Lac-Phe mediates the effects of metformin on food intake and body weight
Abstract
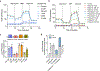
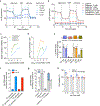
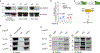
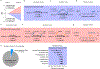
Metformin is a widely prescribed anti-diabetic medicine that also reduces body weight. There is ongoing debate about the mechanisms that mediate metformin's effects on energy balance. Here, we show that metformin is a powerful pharmacological inducer of the anorexigenic metabolite N-lactoyl-phenylalanine (Lac-Phe) in cells, in mice and two independent human cohorts. Metformin drives Lac-Phe biosynthesis through the inhibition of complex I, increased glycolytic flux and intracellular lactate mass action. Intestinal epithelial CNDP2+ cells, not macrophages, are the principal in vivo source of basal and metformin-inducible Lac-Phe. Genetic ablation of Lac-Phe biosynthesis in male mice renders animals resistant to the effects of metformin on food intake and body weight. Lastly, mediation analyses support a role for Lac-Phe as a downstream effector of metformin's effects on body mass index in participants of a large population-based observational cohort, the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Together, these data establish Lac-Phe as a critical mediator of the body weight-lowering effects of metformin.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


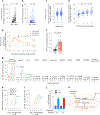
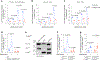

References
-
- Foretz M, Guigas B, Bertrand L, Pollak M & Viollet B Metformin: from mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metab 20, 953–966 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK136526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM113854/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK137889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK116750/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK127073/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL161445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120565/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK116074/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL145095/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

