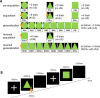
Contingency Reversal in Conditioned Fear Learning: The Moderated Mediation Model of Intolerance of Uncertainty and Instruction
- PMID: 38500554
- PMCID: PMC10945213
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S447426
Contingency Reversal in Conditioned Fear Learning: The Moderated Mediation Model of Intolerance of Uncertainty and Instruction
Abstract
Objective: The study aimed to examine the roles of anxiety and intolerance of uncertainty (IU) in conditioned fear learning under an uncertain context induced by the contingency reversal of the association between the conditioned stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus (CS-US).
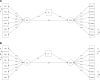
Methods: The study sample comprised 53 participants, randomly divided into two groups: a non-instruction group and an instruction group. The experimental procedure encompassed five stages: pre-acquisition, acquisition, generalization, reversal acquisition, and reversal generalization. Our study primarily focused on analyzing a moderated mediation model.
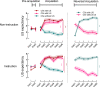
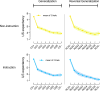
Results: In the instructed group, we observed that the reversed fear generalization response was directly influenced by the pre-reversal fear generalization response, while also being indirectly mediated by the IU factor. However, in the non-instructed group, we did not find a significant mediating effect of IU. Moreover, we noted that the mediation of IU was contingent on the instructional information. It is noteworthy that anxiety did not exhibit a discernible role in conditioned fear within the uncertainty condition in our study.
Conclusion: The findings provide novel insights into fear-related phenomena, emphasizing the intricate interplay between individual traits and fear generalization under conditions of uncertainty. They contribute to understanding the mechanisms of emotional and cognitive interactions in uncertain conditions.
Keywords: associations learning; fear generalization; instructional learning; moderated mediation model.
© 2024 Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human fear conditioning is moderated by stimulus contingency instructions.Biol Psychol. 2021 Jan;158:107994. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2020.107994. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Biol Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33248154 Clinical Trial.
-
Stimulus diversity increases category-based fear generalization and the effect of intolerance of uncertainty.Behav Res Ther. 2022 Dec;159:104201. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2022.104201. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Behav Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36323054
-
An Event-Related Potential Investigation of Fear Generalization and Intolerance of Uncertainty.Behav Ther. 2015 Sep;46(5):661-70. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Behav Ther. 2015. PMID: 26459846
-
Anxiety sensitivity and intolerance of uncertainty facilitate associations between generalized Pavlovian fear and maladaptive avoidance decisions.J Abnorm Psychol. 2019 May;128(4):315-326. doi: 10.1037/abn0000422. Epub 2019 Mar 4. J Abnorm Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30829504
-
Social exclusion influences conditioned fear acquisition and generalization: A mediating effect from the medial prefrontal cortex.Neuroimage. 2020 Sep;218:116735. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116735. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32251834
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources