"It doesn't matter if we're the most amazing professionals in the world…" A qualitative study of professionals' perspectives on parent-child interaction assessment with deaf infants
- PMID: 38500650
- PMCID: PMC10944883
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1315220
"It doesn't matter if we're the most amazing professionals in the world…" A qualitative study of professionals' perspectives on parent-child interaction assessment with deaf infants
Abstract
Introduction: Parent child interaction (PCI) is positively associated with deaf children's language development. However, there are no known, deaf-specific tools to observe how a parent interacts with their deaf child aged 0-3 years. Without a framework for professionals to use with families, it is unknown how professionals assess PCI, what they assess, why they assess, and how the assessment results relate to case management.
Methods: Eighteen hearing and deaf professionals, who work with deaf and hard of hearing infants aged 0-3 years and their families, attended online focus groups. The aim of the study was to gain insight into the professional assessment of PCI. Data were analyzed using thematic analysis.
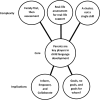
Findings: Six themes were generated from the dataset. Professionals discussed how central parents were in the support offered to families in the home, the importance of knowing and understanding the individual family, and accounting for and supporting parental wellbeing. Descriptions on how to administer a best practice PCI assessment included which parent behaviors to assess and how to make adaptations for different populations. Professionals shared how the assessment and review process could be used to inform and upskill parents through video reflection and goal setting.
Discussion: This study provides insight into the mechanisms and motivations for professionals assessing the interactive behaviors of parents who have deaf children aged 0-3. Professionals acknowledged that family life is multi-faceted, and that support is most meaningful to families when professionals worked with these differences and incorporated them into assessment, goal setting, and intervention plans.
Keywords: assessment; caregiver; deaf; focus groups; infant; parent-child interaction; professional practice.
Copyright © 2024 Curtin, Wakefield, Herman, Morgan and Cruice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Assessing parent-child interaction with deaf and hard of hearing infants aged 0-3 years: An international multi-professional e-Delphi.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 29;19(4):e0301722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301722. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38683866 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing parent interaction with deaf infants: A quantitative survey of UK professional practice.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Jul-Aug;58(4):1148-1167. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12849. Epub 2023 Jan 28. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36708287
-
Assessing parent-child interaction in infant deafness.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 Jun 1;29(3):200-203. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000710. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021. PMID: 33797421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing Parent Behaviours in Parent-Child Interactions with Deaf and Hard of Hearing Infants Aged 0-3 Years: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2021 Jul 29;10(15):3345. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153345. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34362128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Professionals' Perspectives on Supporting Deaf Multilingual Learners and Their Families.J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2021 Jan 1;26(1):70-84. doi: 10.1093/deafed/enaa025. J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2021. PMID: 32842153
Cited by
-
Assessing parent-child interaction with deaf and hard of hearing infants aged 0-3 years: An international multi-professional e-Delphi.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 29;19(4):e0301722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301722. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38683866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun V., Clarke V. (2022). Thematic Analysis: a Practical Guide. London: Sage Publications Ltd.
-
- Brock A. S., Bass-Ringdahl S. M. (2021). Facilitative language techniques used in the home by caregivers of young children who are deaf or hard of hearing. Perspect. ASHA Special Interest Groups 6 1137–1145.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous