Determinants of HIV late presentation among men who have sex with men in Portugal (2014-2019): who's being left behind?
- PMID: 38500732
- PMCID: PMC10947991
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1336845
Determinants of HIV late presentation among men who have sex with men in Portugal (2014-2019): who's being left behind?
Abstract
Introduction: HIV late presentation (LP) remains excessive in Europe. We aimed to analyze the factors associated with late presentation in the MSM population newly diagnosed with HIV in Portugal between 2014 and 2019.
Methods: We included 391 newly HIV-1 diagnosed Men who have Sex with Men (MSM), from the BESTHOPE project, in 17 countrywide Portuguese hospitals. The data included clinical and socio-behavioral questionnaires and the viral genomic sequence obtained in the drug resistance test before starting antiretrovirals (ARVs). HIV-1 subtypes and epidemiological surveillance mutations were determined using different bioinformatics tools. Logistic regression was used to estimate the association between predictor variables and late presentation (LP).
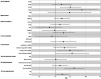
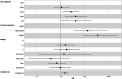
Results: The median age was 31 years, 51% had a current income between 501-1,000 euros, 28% were migrants. 21% had never been tested for HIV before diagnosis, with 42.3% of MSM presenting LP. 60% were infected with subtype B strains. In the multivariate regression, increased age at diagnosis, higher income, lower frequency of screening, STI ever diagnosed and higher viral load were associated with LP.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that specific subgroups of the MSM population, such older MSM, with higher income and lower HIV testing frequency, are not being targeted by community and clinical screening services. Overall, targeted public health measures should be strengthened toward these subgroups, through strengthened primary care testing, expanded access to PrEP, information and promotion of HIV self-testing and more inclusive and accessible health services.
Keywords: HIV-1; Portugal; drug resistance; late presentation; men who have sex with men; vulnerable populations.
Copyright © 2024 Abrantes, Pimentel, Miranda, Silva, Diniz, Ascenção, Piñeiro, Koch, Rodrigues, Caldas, Morais, Faria, Gomes da Silva, Teófilo, Monteiro, Roxo, Maltez, Rodrigues, Gaião, Ramos, Costa, Germano, Simões, Oliveira, Ferreira, Poças, Saraiva da Cunha, Soares, Fernandes, Mansinho, Pedro, Aleixo, Gonçalves, Manata, Mouro, Serrado, Caixeiro, Marques, Costa, Pacheco, Proença, Rodrigues, Pinho, Tavares, Correia de Abreu, Côrte-Real, Serrão, Sarmento e Castro, Nunes, Faria, Baptista, Simões, Mendão, Martins, Gomes, Pingarilho, Abecasis and the BESTHOPE Study Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, WHO regional Office for Europe . HIV/AIDS surveillance in Europe 2022–2021 data. Copenhagen: WHO regional Office for Europe; (2022).
-
- SNS . Infeção por VIH em Portugal – 2023. Lisbon: SNS; (2023).
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, WHO regional Office for Europe . HIV/AIDS surveillance in Europe 2021–2020 data. Stockholm: WHO regional Office for Europe; (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

