Students' Perception of Online Versus Face-to-Face Learning: What Do the Healthcare Teachers Have to Know?
- PMID: 38500946
- PMCID: PMC10948083
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.54217
Students' Perception of Online Versus Face-to-Face Learning: What Do the Healthcare Teachers Have to Know?
Abstract
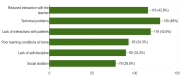
During the COVID-19 pandemic, educational institutions confronted the possibility of complete closure and took countermeasures by adapting e-learning platforms. The present cross-sectional study quantified the impact of the pandemic on medical education using a validated and reliable tool. The tool was used to explore the perceptions of 270 healthcare students about e-learning in comparison to traditional learning systems. Inferential statistics were employed using Pearson's chi-squared test. It was found that e-learning was advantageous because of its location flexibility (46.1%) and the ease of access to study materials (46.5%). However, in-person learning was found to lead to an increase in knowledge (44.9%), clinical skills (52.7%), and social competencies (52.7%). The study concluded that while e-learning offers flexibility, traditional face-to-face teaching is deemed more effective for skill development and social interaction. Hence, e-learning should complement rather than replace traditional methods due to limitations in replicating clinical environments.
Keywords: e-learning; face to face teaching; healthcare education; knowledge; pandemic; perception; skills.
Copyright © 2024, Siddiqui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Suspending classes without stopping learning: China’s education emergency management policy in the COVID-19 outbreak. Zhang W, Wang Y, Yang L, Wang C. J Risk Financial Manag. 2020;13:55.
-
- Integration of a case-based online module into an undergraduate curriculum: what is involved and what is effective? Howlett D, Vincent T, Gainsborough N. e-Learning. 2009;6:372–384.
-
- Report on digital literacy in academic meetings during the 2020 COVID-19 lockdown. Nash C. Challenges. 2020;11:20.
-
- Blended learning versus traditional lecture in introductory nursing pathophysiology courses. Blissitt AM. J Nurs Educ. 2016;55:227–230. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources