Structural determinants of mitochondrial STAT3 targeting and function
- PMID: 38500969
- PMCID: PMC10947224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mitoco.2024.01.001
Structural determinants of mitochondrial STAT3 targeting and function
Abstract
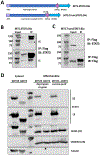
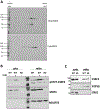
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 has been found within mitochondria in addition to its canonical role of shuttling between cytoplasm and nucleus during cytokine signaling. Mitochondrial STAT3 has been implicated in modulation of cellular metabolism, largely through effects on the respiratory electron transport chain. However, the structural requirements underlying mitochondrial targeting and function have remained unclear. Here, we show that mitochondrial STAT3 partitions between mitochondrial compartments defined by differential detergent solubility, suggesting that mitochondrial STAT3 is membrane associated. The majority of STAT3 was found in an SDS soluble fraction copurifying with respiratory chain proteins, including numerous components of the complex I NADH dehydrogenase, while a minor component was found with proteins of the mitochondrial translation machinery. Mitochondrial targeting of STAT3 required the amino-terminal domain, and an internal linker domain motif also directed mitochondrial translocation. However, neither the phosphorylation of serine 727 nor the presence of mitochondrial DNA was required for the mitochondrial localization of STAT3. Two cysteine residues in the STAT3 SH2 domain, which have been previously suggested to be targets for protein palmitoylation, were also not required for mitochondrial translocation, but were required for its function as an enhancer of complex I activity. These structural determinants of STAT3 mitochondrial targeting and function provide potential therapeutic targets for disrupting the activity of mitochondrial STAT3 in diseases such as cancer.
Keywords: Electron transport chain; Mitochondrial import; Stat3.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akira S, Nishio Y, Inoue M, et al. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994;77:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE. Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994;264:95–98. - PubMed
-
- Raz R, Durbin JE, Levy DE. Acute phase response factor and additional members of the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 family integrate diverse signals from cytokines, interferons, and growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:24391–24395. - PubMed
-
- Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr. STATs: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(9):651–662. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
