Symptom and comorbidity burden in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 38501097
- PMCID: PMC10944929
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1361466
Symptom and comorbidity burden in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is an important but frequently overlooked risk factor for hypertension (HTN). The prevalence of hypertension is high in patients with OSA, but the differences in clinical symptoms and comorbidities between patients with OSA with hypertension and those with normal blood pressure have not been fully defined.
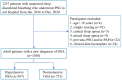
Methods: This study retrospectively analyzed OSA patients diagnosed for the first time in Lihuili Hospital Affiliated to Ningbo University from 2016 to 2020. Patients were divided into an OSA group with hypertension and an OSA group without hypertension. The sociodemographic information, clinical symptoms, comorbidities, and polysomnography results of the two groups were compared. The independent risk factors associated with hypertension in patients with OSA were explored.
Results: A total of 1108 patients with OSA initially diagnosed were included in the study, including 387 with hypertension and 721 without. Compared with OSA patients without hypertension, OSA patients with hypertension were older; had a higher body mass index (BMI) and Epworth sleepiness score (ESS); a higher incidence of nocturia; and a higher proportion of diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, and cerebrovascular disease. Multivariate analysis showed age (odds ratio [OR]:1.06, 95% confidence interval [CI]:1.04-1.08), BMI (OR:1.17, 95% CI:1.11-1.23), ESS score (OR:0.97, 95%CI: 0.94-1.00) and nocturia symptoms (OR:1.64, 95% CI:1.19-2.27) was independently associated with hypertension in OSA patients, and comorbid diabetes (OR: 3.86, 95% CI: 2.31-6.45), coronary heart disease (OR: 1.90, 95% CI:1.15-3.16), and ischemic stroke (OR: 3.69,95% CI:1.31-10.40) was independently associated with hypertension in OSA patients.
Conclusion: Compared to OSA patients with normal blood pressure, OSA patients with hypertension had more significant daytime sleepiness, more frequent nocturnal urination, and a higher risk of diabetes, coronary heart disease, and cerebrovascular disease.
Keywords: comorbidity; daytime sleepiness; hypertension; nocturia; obstructive sleep apnea.
Copyright © 2024 Tao, Dong, Tu, Fang and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epworth Sleepiness Scale may be an indicator for blood pressure profile and prevalence of coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Breath. 2012 Mar;16(1):31-40. doi: 10.1007/s11325-011-0481-5. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Sleep Breath. 2012. PMID: 21243439
-
[Analysis of risk factors and consequences for concurrent obstructive sleep apnea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 12;42(11):832-837. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2019.11.009. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31694093 Chinese.
-
Lower BMI is a predictor of obstructive sleep apnea in elderly Thai hypertensive patients.Sleep Breath. 2013 Dec;17(4):1215-9. doi: 10.1007/s11325-013-0826-3. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Sleep Breath. 2013. PMID: 23443912
-
Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease.Mayo Clin Proc. 2004 Aug;79(8):1036-46. doi: 10.4065/79.8.1036. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004. PMID: 15301332 Review.
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association.Circulation. 2021 Jul 20;144(3):e56-e67. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000988. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 34148375 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Effects of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Sleep Duration on Hypertension in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Study.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 15;13(6):1475. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061475. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564194 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis: An Accomplice in the Induction of Multisystem Complications Triggered by Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 23;14(11):1349. doi: 10.3390/biom14111349. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39595526 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical