Cryo-electron microscopy-based drug design
- PMID: 38501110
- PMCID: PMC10945328
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1342179
Cryo-electron microscopy-based drug design
Abstract
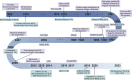
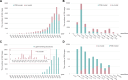
Structure-based drug design (SBDD) has gained popularity owing to its ability to develop more potent drugs compared to conventional drug-discovery methods. The success of SBDD relies heavily on obtaining the three-dimensional structures of drug targets. X-ray crystallography is the primary method used for solving structures and aiding the SBDD workflow; however, it is not suitable for all targets. With the resolution revolution, enabling routine high-resolution reconstruction of structures, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has emerged as a promising alternative and has attracted increasing attention in SBDD. Cryo-EM offers various advantages over X-ray crystallography and can potentially replace X-ray crystallography in SBDD. To fully utilize cryo-EM in drug discovery, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of this technique and noting the key advancements in the field are crucial. This review provides an overview of the general workflow of cryo-EM in SBDD and highlights technical innovations that enable its application in drug design. Furthermore, the most recent achievements in the cryo-EM methodology for drug discovery are discussed, demonstrating the potential of this technique for advancing drug development. By understanding the capabilities and advancements of cryo-EM, researchers can leverage the benefits of designing more effective drugs. This review concludes with a discussion of the future perspectives of cryo-EM-based SBDD, emphasizing the role of this technique in driving innovations in drug discovery and development. The integration of cryo-EM into the drug design process holds great promise for accelerating the discovery of new and improved therapeutic agents to combat various diseases.
Keywords: cryo-electron microscopy; drug development; high-resolution; single particle analysis; structure-based drug design.
Copyright © 2024 Cebi, Lee, Subramani, Bak, Oh and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- A low-cost electron microscope maps proteins at speed (2023). A low-cost electron microscope maps proteins at speed. Nature 624 (7990), 11. 10.1038/d41586-023-03748-2 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

