Layered Double Hydroxides: Recent Progress and Promising Perspectives Toward Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 38501901
- PMCID: PMC11132086
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202306035
Layered Double Hydroxides: Recent Progress and Promising Perspectives Toward Biomedical Applications
Abstract
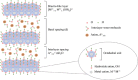
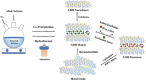
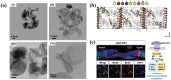
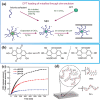
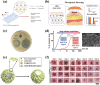
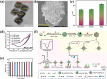
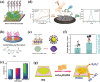
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) have been widely studied for biomedical applications due to their excellent properties, such as good biocompatibility, degradability, interlayer ion exchangeability, high loading capacity, pH-responsive release, and large specific surface area. Furthermore, the flexibility in the structural composition and ease of surface modification of LDHs makes it possible to develop specifically functionalized LDHs to meet the needs of different applications. In this review, the recent advances of LDHs for biomedical applications, which include LDH-based drug delivery systems, LDHs for cancer diagnosis and therapy, tissue engineering, coatings, functional membranes, and biosensors, are comprehensively discussed. From these various biomedical research fields, it can be seen that there is great potential and possibility for the use of LDHs in biomedical applications. However, at the same time, it must be recognized that the actual clinical translation of LDHs is still very limited. Therefore, the current limitations of related research on LDHs are discussed by combining limited examples of actual clinical translation with requirements for clinical translation of biomaterials. Finally, an outlook on future research related to LDHs is provided.
Keywords: biomedical application; drug delivery; exchangeability; layered double hydroxides; nanotheranostics.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
P.v.R also is a co‐founder, scientific advisor, and shareholder in BiomACS BV, a biomedical‐oriented screening company. The authors declare no other conflict of interest. The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

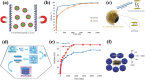

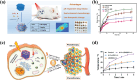

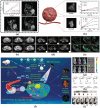
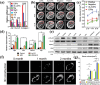


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
