The effect of lacosamide on calcitonin gene-related peptide serum level in episodic migraine patients: a randomized, controlled trial
- PMID: 38502425
- PMCID: PMC11139685
- DOI: 10.1007/s13760-024-02499-9
The effect of lacosamide on calcitonin gene-related peptide serum level in episodic migraine patients: a randomized, controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Migraine affects 11-15% of people worldwide, and the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is released during the migraine attack, producing pulsating pain of migraine. Also, lacosamide reacts with collapsin-response mediator protein 2, preventing its phosphorylation and leading to the inhibition of CGRP release in the trigeminal system.
Objective: The primary outcome was the difference in the serum level of CGRP-LI after three months of treatment with either lacosamide and ibuprofen or ibuprofen alone in episodic migraine patients. The secondary outcomes were assessing safety and efficacy of lacosamide in episodic migraine patients.
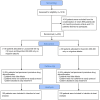
Methods: We conducted an open-label randomized controlled trial on episodic migraine patients aged 10-55 years diagnosed according to (ICHD-3) in Kafr El-Sheikh University Hospital, Egypt. We assessed serum levels of CGRP-LI before and three months after treatment in our two groups, the lacosamide, and the control groups. We also assessed the side effects of treatment in each group, the percentage of patients who achieved ≥ 50% reduction in the migraine monthly days (MMD) frequency and the percentage of patients who achieved pain freedom within 2 h in ≥ 4 of 5 attacks in each group.
Results: 200 episodic migraine patients completed the study. There was a statistically significantly higher reduction in the serum CGRP-LI level in the lacosamide group compared with the control group. In addition, lacosamide was well tolerated by patients. Also, the lacosamide group had statistically significant higher percentage of patients who achieved ≥ 50% reduction in the migraine monthly days (MMD) frequency and pain freedom within two hours in ≥ 4 of 5 attacks with P-values 0.002, 0.02 respectively.
Conclusion: The daily use of lacosamide 50 mg Bid for three months in episodic migraine patients was associated with a significant reduction in serum CGRP-LI, better clinical outcomes regarding frequency and duration of migraine attacks, and was well tolerated by patients. These results were derived from an open-label pilot study that needed to be thoroughly investigated by a large-scale, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study.
Trial registration: We registered our trial on ClinicalTrials.gov, named after "The Lacosamide's Effect on Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide in Migraine Patients," and with a clinical trial number (NCT05632133)-August 8, 2023.
Keywords: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; Egypt; Episodic migraine; Lacosamide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Similar articles
-
The effects of vitamin D supplementation on interictal serum levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in episodic migraine patients: post hoc analysis of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial.J Headache Pain. 2020 Feb 24;21(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01090-w. J Headache Pain. 2020. PMID: 32093657 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Infusion of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide on Cluster Headache Attacks: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 1;75(10):1187-1197. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.1675. JAMA Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29987329 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody for episodic migraine: a meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2018 Dec;39(12):2097-2106. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3547-3. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30182284
-
Indirect Comparison of Topiramate and Monoclonal Antibodies Against CGRP or Its Receptor for the Prophylaxis of Episodic Migraine: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.CNS Drugs. 2021 Aug;35(8):805-820. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00834-9. Epub 2021 Jul 16. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34272688 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Galcanezumab for the Preventive Treatment of Migraine: A Narrative Review.Adv Ther. 2020 May;37(5):2034-2049. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01319-9. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32319039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A multicenter trial on the predictors of different subtypes of hemorrhagic infarction after thrombolysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 30;14(1):29822. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76189-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39616189 Free PMC article.
-
Cilostazole versus clopidogrel in acute large-vessel moderate and moderate-to-severe ischemic stroke: a randomized controlled trial.Neurol Sci. 2025 Aug;46(8):3973-3986. doi: 10.1007/s10072-025-08107-9. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40232632 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CILO-CLOP Trial: Cilostazol Versus Clopidogrel in Acute Moderate and Moderate-to-Severe Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Multicenter Trial.Neurol Ther. 2025 Jun;14(3):927-948. doi: 10.1007/s40120-025-00739-5. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Neurol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40220202 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of lacosamide on cortical spreading depolarization in mice.J Headache Pain. 2025 Jul 16;26(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02099-9. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40670944 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials