Exploring the Low-Dose Limit for Focal Hepatic Lesion Detection with a Deep Learning-Based CT Reconstruction Algorithm: A Simulation Study on Patient Images
- PMID: 38502435
- PMCID: PMC11522246
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01080-3
Exploring the Low-Dose Limit for Focal Hepatic Lesion Detection with a Deep Learning-Based CT Reconstruction Algorithm: A Simulation Study on Patient Images
Abstract
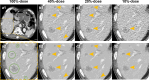
This study aims to investigate the maximum achievable dose reduction for applying a new deep learning-based reconstruction algorithm, namely the artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction (AIIR), in computed tomography (CT) for hepatic lesion detection. A total of 40 patients with 98 clinically confirmed hepatic lesions were retrospectively included. The mean volume CT dose index was 13.66 ± 1.73 mGy in routine-dose portal venous CT examinations, where the images were originally obtained with hybrid iterative reconstruction (HIR). Low-dose simulations were performed in projection domain for 40%-, 20%-, and 10%-dose levels, followed by reconstruction using both HIR and AIIR. Two radiologists were asked to detect hepatic lesion on each set of low-dose image in separate sessions. Qualitative metrics including lesion conspicuity, diagnostic confidence, and overall image quality were evaluated using a 5-point scale. The contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) for lesion was also calculated for quantitative assessment. The lesion CNR on AIIR at reduced doses were significantly higher than that on routine-dose HIR (all p < 0.05). Lower qualitative image quality was observed as the radiation dose reduced, while there were no significant differences between 40%-dose AIIR and routine-dose HIR images. The lesion detection rate was 100%, 98% (96/98), and 73.5% (72/98) on 40%-, 20%-, and 10%-dose AIIR, respectively, whereas it was 98% (96/98), 73.5% (72/98), and 40% (39/98) on the corresponding low-dose HIR, respectively. AIIR outperformed HIR in simulated low-dose CT examinations of the liver. The use of AIIR allows up to 60% dose reduction for lesion detection while maintaining comparable image quality to routine-dose HIR.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction; Computed tomography; Dose reduction; Hepatic lesion.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Image quality assessment of artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction for low dose unenhanced abdomen: comparison with hybrid iterative reconstruction.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jul;50(7):3353-3362. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04760-4. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39707032
-
Image quality assessment of artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction for low dose aortic CTA: A feasibility study of 70 kVp and reduced contrast medium volume.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Apr;149:110221. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110221. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35196615
-
Diagnostic CT of colorectal cancer with artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction: A clinical evaluation.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Feb;171:111301. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111301. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38237522
-
Deep-learning CT reconstruction in clinical scans of the abdomen: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023 Aug;48(8):2724-2756. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-03966-2. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023. PMID: 37280374 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Relationship Between Artificial Intelligence and CT Radiation Dose.Acad Radiol. 2022 Nov;29(11):1709-1719. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.10.024. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34836775 Review.
Cited by
-
Image quality assessment of artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction for low dose unenhanced abdomen: comparison with hybrid iterative reconstruction.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jul;50(7):3353-3362. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04760-4. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39707032
-
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) planning CT on 8-cm detector scanners: Proper dose control by combined use of two deep-learning reconstruction algorithms.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Sep;26(9):e70224. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70224. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40883100 Free PMC article.
-
One-stop combined coronary-craniocervical computed tomography angiography with low-dose body coverage using artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction: a clinically feasible solution to multi-territorial atherosclerosis diagnosis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Feb 1;15(2):1516-1527. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1545. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 39995738 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm Combined with Low-Dose Aortic CTA for Preoperative Access Assessment of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: A Prospective Cohort Study.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Aug 6. doi: 10.1007/s10278-025-01622-3. Online ahead of print. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 40768017
-
The utility of low-dose pre-operative CT of ovarian tumor with artificial intelligence iterative reconstruction for diagnosing peritoneal invasion, lymph node and hepatic metastasis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 May 13. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04977-x. Online ahead of print. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40358704
References
-
- Volders D, Bols A, Haspeslagh M, Coenegrachts K. Model-based iterative reconstruction and adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction techniques in abdominal CT: comparison of image quality in the detection of colorectal liver metastases. Radiology. 2013;269(2):469–474. 10.1148/radiol.13130002 - PubMed
-
- Solomon J, Marin D, Roy Choudhury K, Patel B, Samei E. Effect of Radiation Dose Reduction and Reconstruction Algorithm on Image Noise, Contrast, Resolution, and Detectability of Subtle Hypoattenuating Liver Lesions at Multidetector CT: Filtered Back Projection versus a Commercial Model-based Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm. Radiology. 2017;284(3):777–787. 10.1148/radiol.2017161736 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Singh R, Digumarthy SR, Muse VV, et al. Image Quality and Lesion Detection on Deep Learning Reconstruction and Iterative Reconstruction of Submillisievert Chest and Abdominal CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;214(3):566–573. 10.2214/AJR.19.21809 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
