Association of thyroid autoantibodies and diabetic kidney disease in hospitalised patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study from a Chinese university hospital
- PMID: 38503411
- PMCID: PMC10952948
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077338
Association of thyroid autoantibodies and diabetic kidney disease in hospitalised patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study from a Chinese university hospital
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse and explore the association between thyroid autoantibodies and diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Design: A cross-sectional study.
Setting: Patients were from the inpatient unit at The Second Endocrinology Department of Shengjing Hospital Affiliated to China Medical University (Shenyang, China) between January 2015 and September 2019.
Participants: A total of 150 Chinese adults with T2DM were included in the study, including 83 men and 67 women. Their age ranged between 25 and 92 years.
Methodology: They grouped by the presence of DKD, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), estimated glomerular filtration rate, and levels of thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) and thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb). Data on the patients' general characteristics and laboratory measurements (levels of fasting plasma glucose, glycated haemoglobin, and albumin; renal function; and thyroid function) were collected. Binary logistic regression was performed to identify risk factors for DKD.
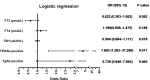
Results: The level of TPOAb, the positivity rates of TPOAb (p<0.01) and TgAb (p<0.05) were higher in patients with DKD than in those without DKD. The TPOAb level in patients with a UACR<30 mg/g creatinine was lower than that in patients with a UACR between 30 and 300 mg/g creatinine (p<0.05). The prevalence of DKD was higher in patients with a TPOAb-positive or TgAb-positive status. The result of binary logistic regression analysis showed that a TPOAb-positive status was significantly associated with DKD in patients with T2DM (OR=7.683, 95% CI 1.583 to 37.286, p<0.05).
Conclusions: TPOAb-positive status is in association with DKD in patients with T2DM. Large scale, prospective cohort studies are warranted to confirm our findings.
Keywords: diabetes & endocrinology; diabetic nephropathy & vascular disease; thyroid disease.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Elevated thyroid autoantibodies as risk factors for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 5;15:1478818. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1478818. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39703861 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Thyroid Autoantibodies with Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Dec;30(12):374-380. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38518164
-
Correlation of serum thyrotropin and thyroid hormone levels with diabetic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Aug 30;24(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01699-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39215277 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Parameters and Kidney Disorder in Type 2 Diabetes: Results from the METAL Study.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Mar 28;2020:4798947. doi: 10.1155/2020/4798947. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32337292 Free PMC article.
-
Association between thyroid autoimmunity and bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study.Endocrine. 2024 Aug;85(2):604-614. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-03733-3. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 38393508
Cited by
-
Mediating role of triglyceride-glucose index and its derivatives in the relationship between central obesity and Hashimoto thyroiditis in type 2 diabetes.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Dec 19;23(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02402-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39702130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. . Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International diabetes Federation diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019;157:S0168-8227(19)31230-6. 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
